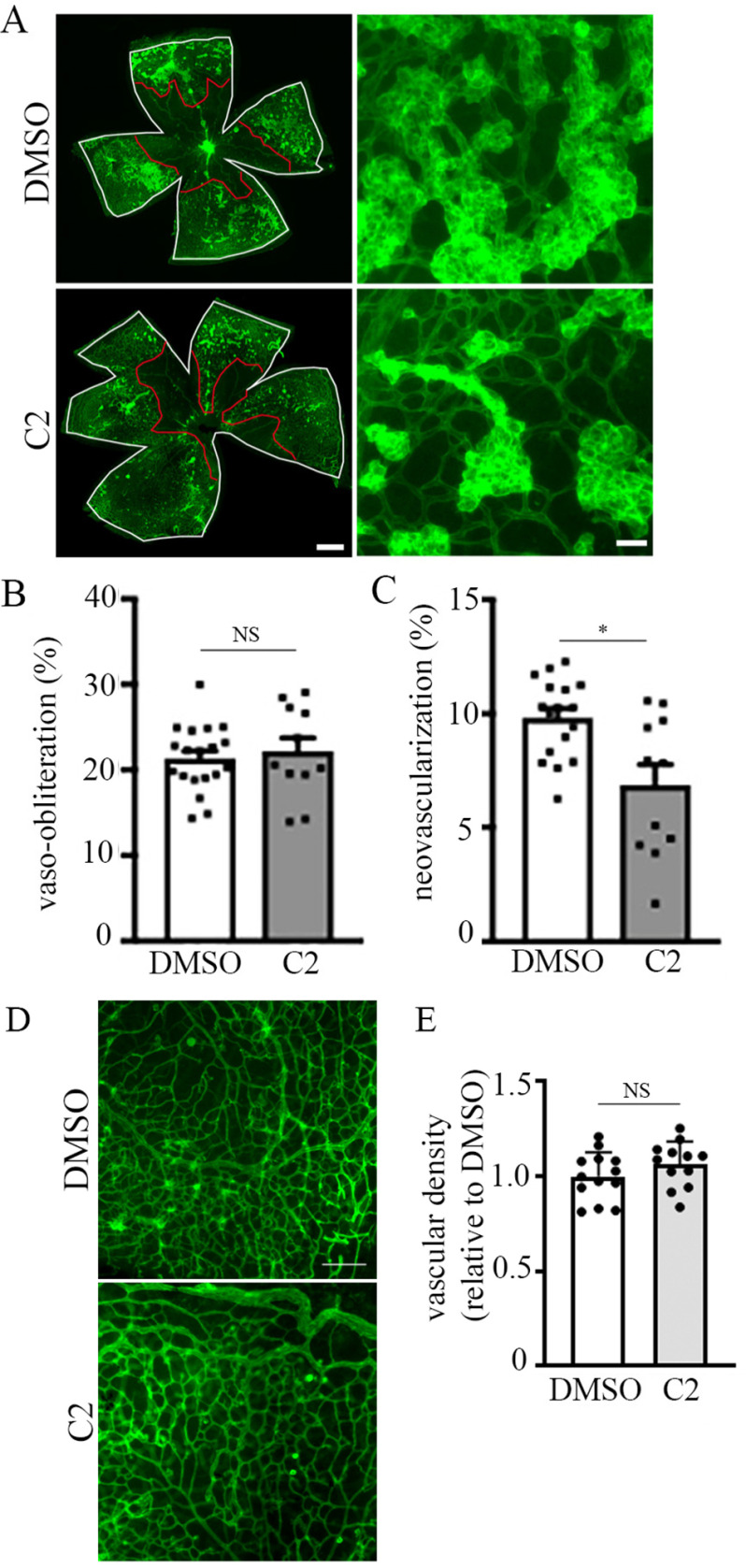
Figure 6.
Small molecule inhibitor of PFN1–actin interaction attenuates angiogenesis associated with oxygen-induced retinopathy. A, lower (left panels) and higher (right panels) magnification microphotographs of FITC-coupled BS-1 lectin-stained retina of P17-OIR C57BL/6JRj mice after intravitreal injection at P12 and P14 of DMSO (1 µl) (upper panels) or C2 (1 µl of 500 µm solution) (lower panels). VO areas are highlighted in red, and total retinal area is in white. The scale bars in the left and right panels indicate 80 and 50 μm, respectively. B and C, quantification of VO (B) and NV (C) in P17 control versus C2-treated retinal at-mounts). D and E, representative images (D; scale bar, 100 μm) and quantification (E) of vascular density in P17 control versus C2-treated retinal flat mounts in non–vaso-obliterated and tuft-free areas. A total of 11 retinae from two independent experiments in each group were analyzed. *, p < 0.05; NS, not significant (Mann–Whitney t test).