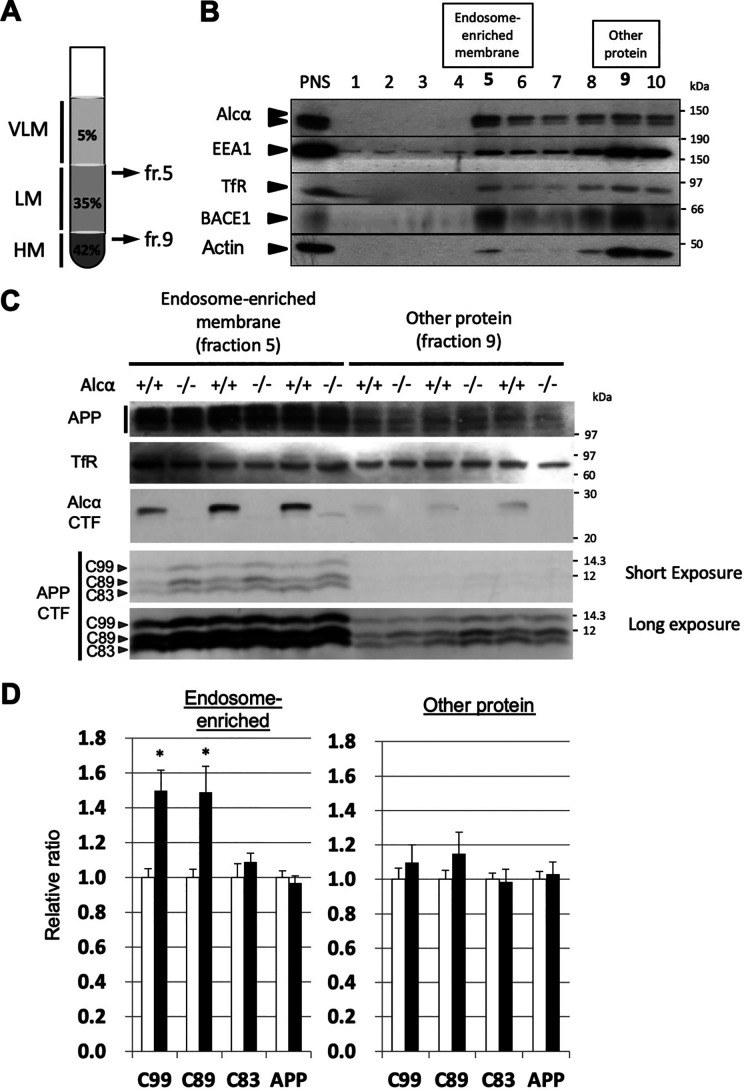
Figure 6.
Increased β-site cleavages of APP in the endosome-enriched fraction of Alcα-deficient mouse brains. A, preparation of endosome-enriched membrane fraction. Post-nuclear supernatant (PNS) prepared from brain homogenate was adjusted to 42.5% sucrose and set at the bottom. Buffer with 35% sucrose was overlaid, and the same buffer with 5% sucrose was subsequently applied as shown in the figure. Very light membrane (VLM) largely composed of late endosomes entered the 5% sucrose layer, and heavy membrane (HM)-containing plasma membrane and rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane with cytosol proteins resided in the 42.5% sucrose layer. Light membrane (LM)-containing early endosomes with Golgi and other membranes accumulated underneath the interface between 5 and 35% sucrose layers after ultracentrifugation. See Fig. S5 for briefly illustrated preparation scheme. B, typical isolation of endosome-enriched fraction from WT mouse hippocampus and cerebral cortex. The endosome-enriched fraction (fr. 5) and other protein fractions (fr. 9) are shown in boldface type. PNS and the respective fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to detect indicated proteins. Some EEA1 and BACE1 resided in the endosome-enriched fraction 5. ∼10% of the protein was separated in fraction 5, and ∼80% of protein resided in fractions 9 and 10 (Fig. S5). TfR, transferrin receptor. C, immunoblot analysis of the endosome-enriched (fr. 5) and other protein (fr. 9) fractions of WT and Alcα-deficient mouse brains. Samples of WT (+/+) and Alcα-deficient (−/−) mice were analyzed with antibodies to detect the indicated proteins. D, the band densities of APP and APP CTFs in C were quantified and standardized against transferrin receptor. The value of WT was assigned a reference value of 1.0. Statistical significance was analyzed using three independent experiments (n = 3 mice/group; unpaired t test; *, p < 0.05). Data represent means ± S.E. (error bars). APP, mature APP plus immature APP; C99, CTFβ; C89, CTFβ′; C83, CTFβ of APP CTFs.