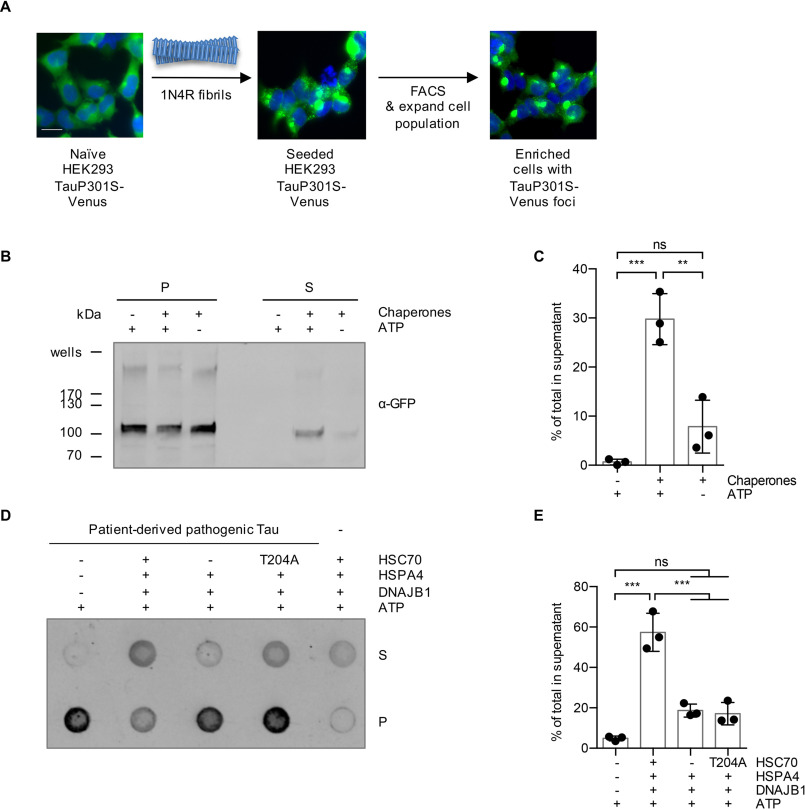
Figure 3.
Sarkosyl-insoluble TauP301S-Venus aggregated in a cell culture model and Tau aggregates extracted from AD brain are substrates for the disaggregation machinery. A, a HEK293 0N4R TauP301S-Venus cell line was used to generate a cell population with Tau aggregates as outlined in the depicted workflow. Naïve cells were seeded with 1N4R fibrils, followed by the enrichment of focus-containing cells by FACS. A representative image of the seeded cell population after the FACS enrichment is shown. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Sarkosyl-insoluble TauP301S-Venus material extracted from the seeded HEK293 cell population was subjected to in vitro disaggregation assays with the recombinant human Hsp70 disaggregation machinery (HSC70, DNAJB1, HSPA4) ± ATP for 20 h at 30 °C. S and P fractions were separated by centrifugation at 337,000 × g and analyzed by immunoblotting with an α-GFP antibody detecting TauP301S-Venus. C, densitometric quantification of TauP301S-Venus in S fractions compared with the total (S + P) of the Western blot shown in panel B. n = 3, mean ± S.D. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. ns, not significant; ***, p ≤ 0.001. D, the Sarkosyl-insoluble fraction extracted from an AD brain was subjected to in vitro disaggregation assays for 20 h at 30 °C. The samples were treated either with the complete disaggregation machinery (HSC70, DNAJB1, HSPA4), with only DNAJB1 and HSPA4, omitting HSC70, or with DNAJB1 and HSPA4 together with an ATPase-defective mutant HSC70 (T204A). S and P fractions were separated by centrifugation at 150,000 × g and analyzed by dot blotting with the α-Tau antibody HT7. E, densitometric quantification of the dot blot shown in panel D. The percentage of Tau in S fractions compared with the total (S + P) was calculated for each sample. The background signal of chaperones without patient material was subtracted. n = 3, mean ± S.D. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test was used. ns, not significant; ***, p ≤ 0.001.