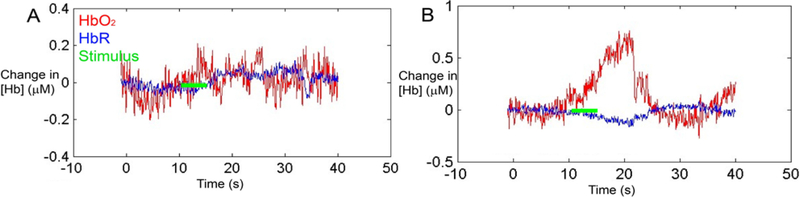
Figure 3. Representative measurements from the auditory cortex in a deaf child in response to auditory stimulation on the day of cochlear implant activation.
(A) Before cochlear implant activation, auditory stimulation (green line) produced no changes in oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2 (red) and HbR (blue), respectively). (B) Immediately after cochlear implant activation, auditory stimulation evoked an increase in HbO2 and a decrease in HbR. This is the expected hemodynamic response to an increase in neuronal activity.