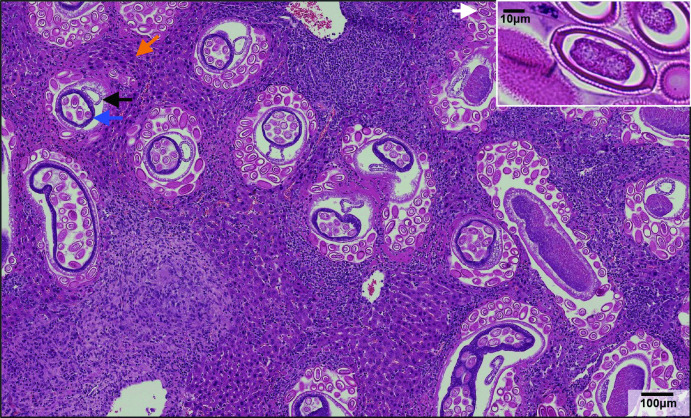
Fig. 4.
Haematoxylin and eosin-stained section of liver from a mouse heavily infected with C. hepatica. Adult worms (blue arrow, ovum containing eggs; black arrow, intestine) and free eggs (white arrow) were located within the liver parenchyma and associated with multifocal to coalescent granulamatomous inflammation with central necrosis and multinucleated giant cells (orange arrow). This microscopic finding corresponded to the enlarged liver and areas of pallor depicted in Fig. 3. Insert: C. hepatica egg with characteristic bipolar plugs.