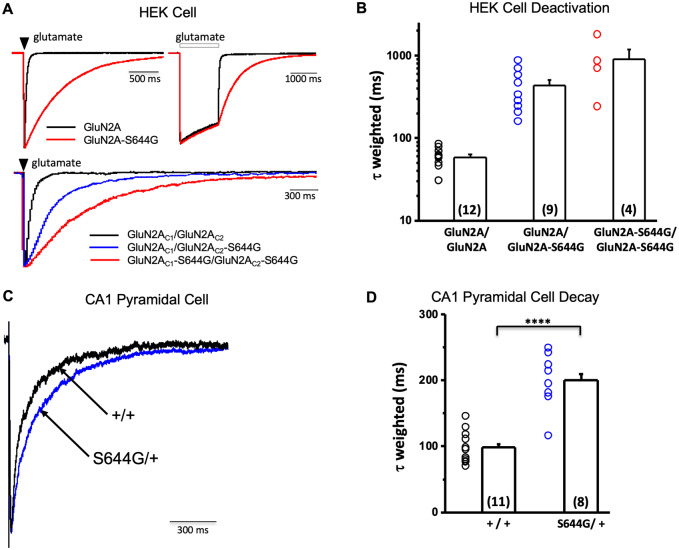
Figure 5.
GluN2A-S644G NMDAR response time course in vitro and synaptic time course in acute hippocampal slices. (A) Top: Representative GluNl/GluN2A (black) or GluN1/GluN2A-S644G (red) whole cell current time course in response to brief (1–5 ms, left) or prolonged (2 s, right) application of maximally effective concentrations of glutamate (100 μM) and glycine (30 μM). Bottom: The response for triheteromeric GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2AC2 receptors that contained 0 (black), 1 (blue) or 2 (red) copies of the S644G mutation (brief pulses 20–50 ms; traces corrected for series resistance using ChanneLabv2 software) (Traynelis, 1998) (statistics are given in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 2). (B) Mean ± SEM for the weighted tau describing deactivation for NMDARs expressed in HEK cells. (C) Superimposed, normalized evoked NMDAR-mediated component of the EPSC onto CA1 pyramidal cells in hippocampal slices from wild-type +/+ and +/S644G mice. (D) Mean ± SEM for the weighted tau describing synaptic decay of the NMDAR-mediated current component of the EPSC onto CA1 pyramidal cells in +/+ (99 ± 7.4 ms, n = 11 cells) and S644G/+ (200 ± 15 ms, n = 8 cells) slices show a statistically significant prolongation in the S644G/+ condition (Student’s two-sample t-test, t = 6.5, P = 0.0000053). The NMDAR-mediated charge transfer onto CA1 pyramidal cells was also significantly increased in the S644G/+ mouse (125 ± 30 pC/pF for +/+ versus 351 ± 81 pC/pF for S644G/+; Student’s two-sample t-test, t = 2.93, P = 0.00935; data not shown). However, peak amplitude of the evoked EPSC was not significantly different between the two genotypes (−158 pA ± 39 pA for +/+ versus −178 ± 24 pA for S644G/+; Student’s two-sample t-test, t = 0.39, P = 0.71; data not shown). Other kinetic parameters of the NMDAR-mediated EPSC are as follows and were not tested for statistical significance: taufast (49 ± 6 ms for +/+ versus 100 ± 9 ms for S644G/+), tauslow (266 ± 35 ms for +/+ versus 1143 ± 23 ms for S644G/+), %fast (71 ± 3.3 for +/+ versus 75 ± 5.1 for S644G/+), and rise time (7.1 ± 0.4 ms for +/+ versus 7.6 ± 0.6 ms for S644G/+). ****P < 0.00001.