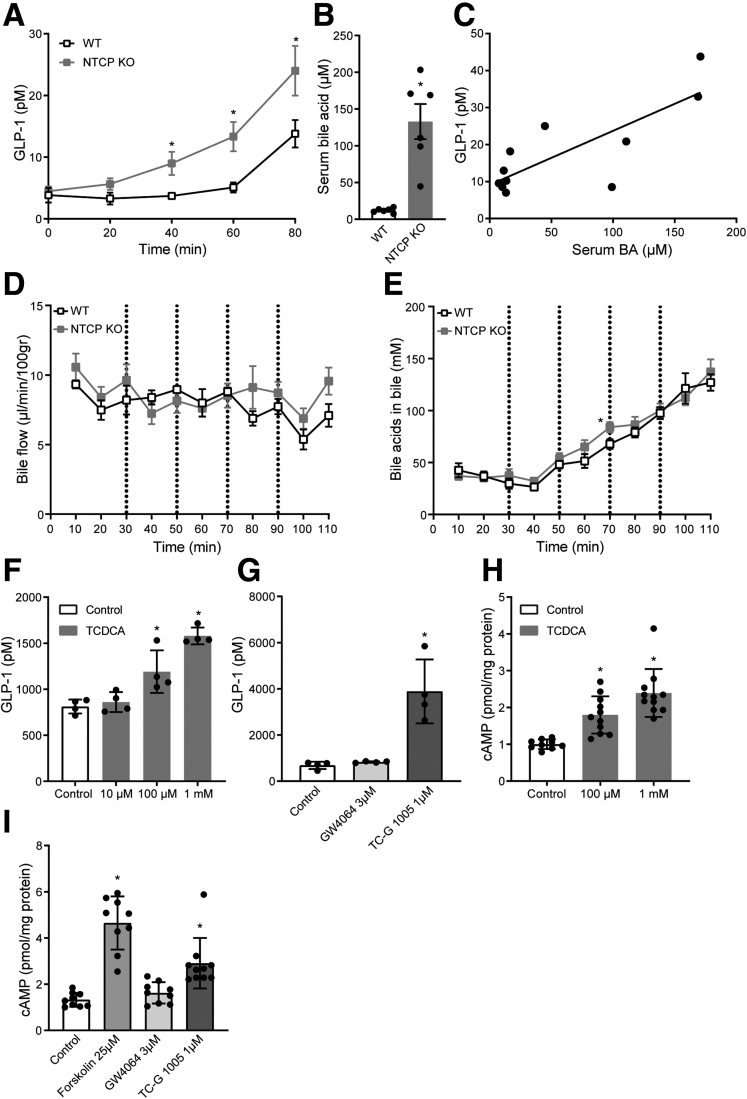
Figure 2.
Conjugated bile acids stimulate GLP-1 secretion. (A) Plasma GLP-1 during and (B) total bile acids after the intravenous infusion of bile acid TC (150–600 nmol/min, 0.1- to 0.4-mL/h infusion rate) in WT or NTCP KO mice (n = 10–12). (C) Scatterplot showing the significant correlation between plasma levels of GLP-1 (y-axis) and bile acids (x-axis). Values are determined at the last time point in the TC intravenous infusion experiment. (D) Bile flow and (E) bile acid concentration in bile during the intravenous infusion of bile acid TC (150–600 nmol/min, 0.1- to 0.4-mL/h infusion rate) in WT or NTCP KO mice (n = 10–12). (F) GLP-1 secretion of GLUTag cells after a 2-hour treatment with bile acid TCDCA or (G) TGR5 agonist TC-G 1005 and FXR agonist GW4064 (representative results of 3 independent experiments, n = 4 wells/group). Two-minute cAMP secretion of GLUTag cells treated with (H) TCDCA or (I) TC-G 1005, GW4064, or positive control forskolin. Samples were normalized to protein content, results of 3 independent experiments (n = 9–11). Error bars show (A–E) SEM or (F–I) SD. Asterisk indicates significant changes compared with the control group.