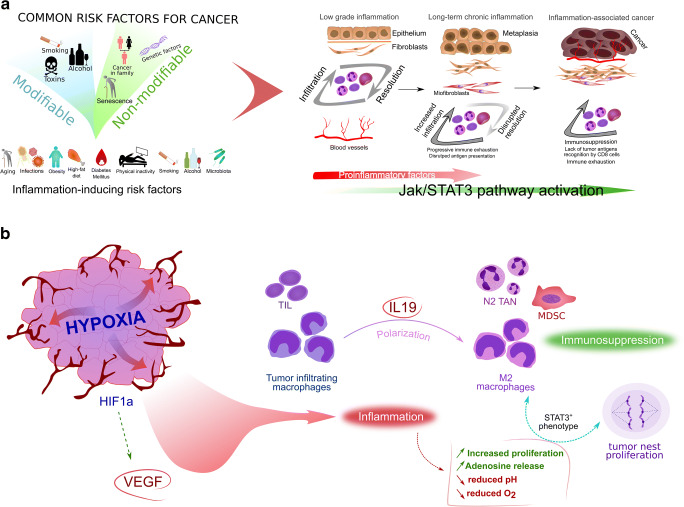
Fig. 1.
A proposed simplified model of the association between inflammation and oncogenesis. A. Common risk factors for cancers described in the text and their proinflammatory potential. Inflammation can be triggered by risk factors for cancer and long-term exposure to these factors can lead to permanent changes in cell structure and signaling associated with neoplastic transformation. B Hypoxia and proangiogenic activity are responsible for modifying the tumor microenvironment. The secretory activity of cancer cells leads to a change in the polarization of immune cells, which increases immunosuppression and causes cancer progression