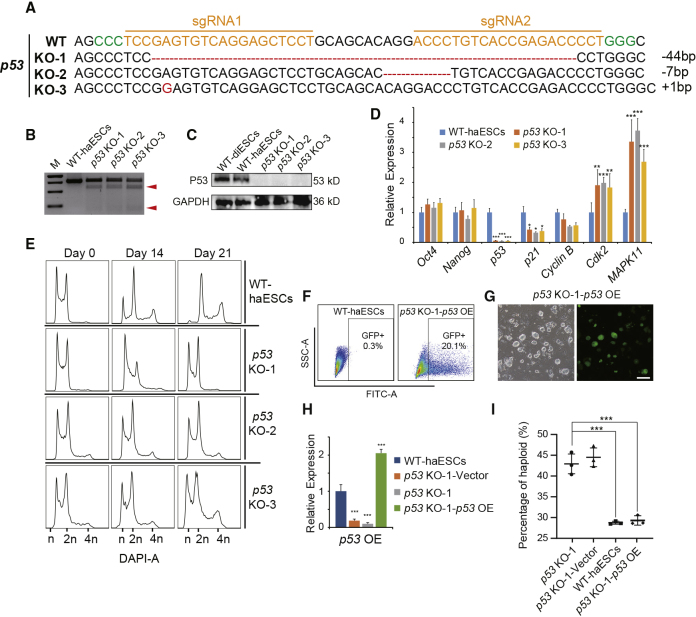
Figure 1.
p53 Deletion in haESC and DNA Analysis during Proliferation
(A). p53-deleted genotypes in subclones p53 KO-1, p53 KO-2, and p53 KO-3.
(B) T7ENI cleavage analysis of the p53-KO lines p53 KO-1, p53 KO-2, and p53 KO-3. Cleaved products (red arrowheads) indicate the presence of mutations.
(C) Western blotting to detect P53 in WT-diESCs, WT-haESCs, p53 KO-1, p53 KO-2, and p53 KO-3 cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
(D) Expression levels of pluripotent, p53-related, and cell-cycle-related genes (Oct4, Nanog, p53, p21, CyclinB, Cdk2, and MAPK11) in WT-haESCs, p53 KO-1, p53 KO-2, and p53 KO-3 cells determined by qPCR (n = 3 independent experiments). Data presented as mean ± SEM. t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(E) DNA content analysis of p53-KO haESCs during culture on day 0, day 14, and day 21 without sorting, with WT-haESCs as a control. The percentages of the 1n (G0/G1) peak in WT-haESCs were 27.4%, 9.33%, and 2.4%, respectively; in p53 KO-1 cells, 23.5%, 22.8%, and 21.4%, respectively; in p53 KO-2 cells, 23.6%, 21.1%, and 20.9%, respectively; in p53 KO-3 cells, 23.7%, 21.5%, and 20.2%, respectively.
(F) Percentage of GFP+ cells in p53 KO-1-p53 OE cells after transfection. WT-haESCs without transfection were used as a negative control.
(G) Bright-field (BF) and FITC images of p53 KO-1-p53 OE cells, Scale bar, 100 μm.
(H) Expression levels of p53 in WT-haESCs, p53 KO-1-Vector, p53 KO-1, and p53 KO-1-p53 OE cells determined by qPCR (n = 3 independent experiments). Data presented as mean ± SEM. t test: ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(I) Percentages of haploids in p53 KO-1, p53 KO-1-Vector, WT-haESCs, and p53 KO-1-p53 OE cells 10 days after sorting. Nearly 44% of sorted cells remained in haploidy in p53 KO-1 and p53 KO-1-Vector group, whereas WT-haESCs and p53 KO-1-p53 OE exhibited only 29% staying as haploid cells (n = 3 independent experiments). Data presented as mean ± SEM. t test: ∗∗∗p < 0.001.