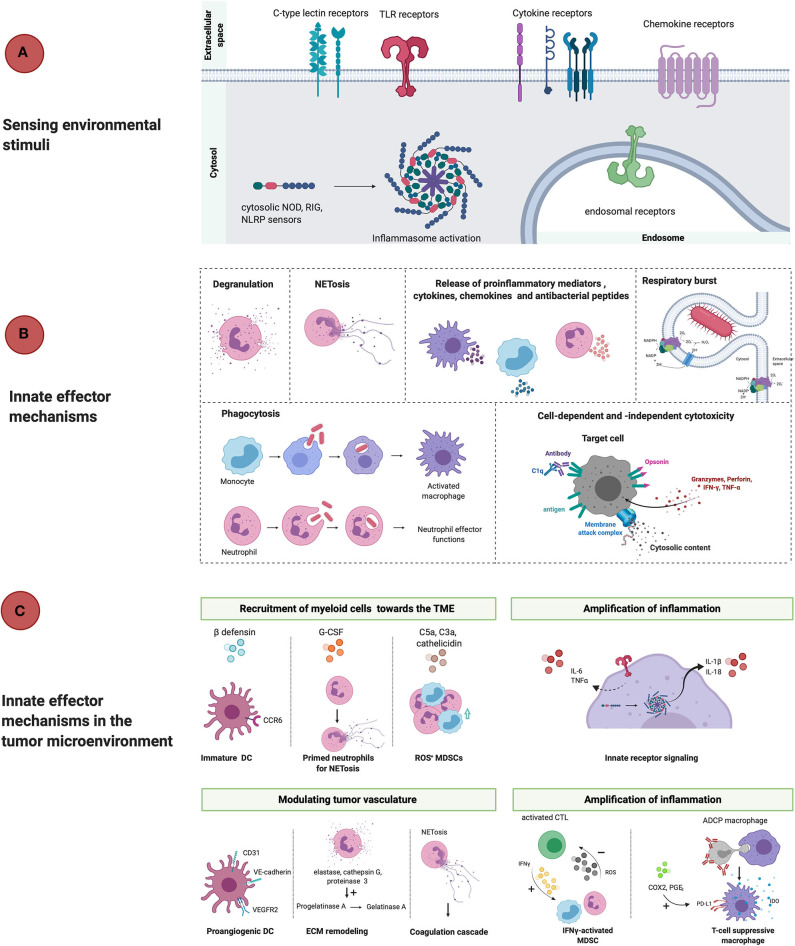
Figure 1.
Linear representation of classical innate immunity in response to threats and in the TME. (A) PAMPs and DAMPs are recognized by surface-expressed, endosomal and cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (TLR, CLR, cytokine, chemokine receptors, NLRP3) which results in phenotypical changes that counteract ongoing threats or tissue damage. (B) Effector mechanisms that take place during inflammation are degranulation, NETosis, release of proinflammatory mediators, respiratory burst, phagocytosis and cell-dependent and -independent cytotoxicity. The net result is the recruitment of immunocompetent cells that mount an inflammatory reaction and potentially resolve the infection. (C) However, in the tumor microenvironment innate myeloid cells promote tumor progression through active recruitment to the TME in response to ß-defensins, cathelicidin, G-CSF, complement factors and chemokines. Once arrived in the TME, myeloid cells are activated and release proinflammatory mediators, which empowers tumor-associated inflammation. Activation of myeloid cells also allows for remodeling of the tissue vasculature and extracellular matrix, which also allows for cancer-cell invasion and metastasis. Furthermore, myeloid cells contribute to immunosuppression once activated by for example, upregulation of PD-L1 and IDO release during antibody-dependent phagocytosis of target cells or stimulatory cytokines (IFNγ). DC, dendritic cell; ECM, extracellular matrix; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; IFNγ, interferon gamma; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; ADCP, antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; COX2, cyclooxygenase 2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; G-CSF, granulocyte colony stimulating factor; NOD, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; RIG, retinoic acid-inducible gene; NLRP, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain containing.