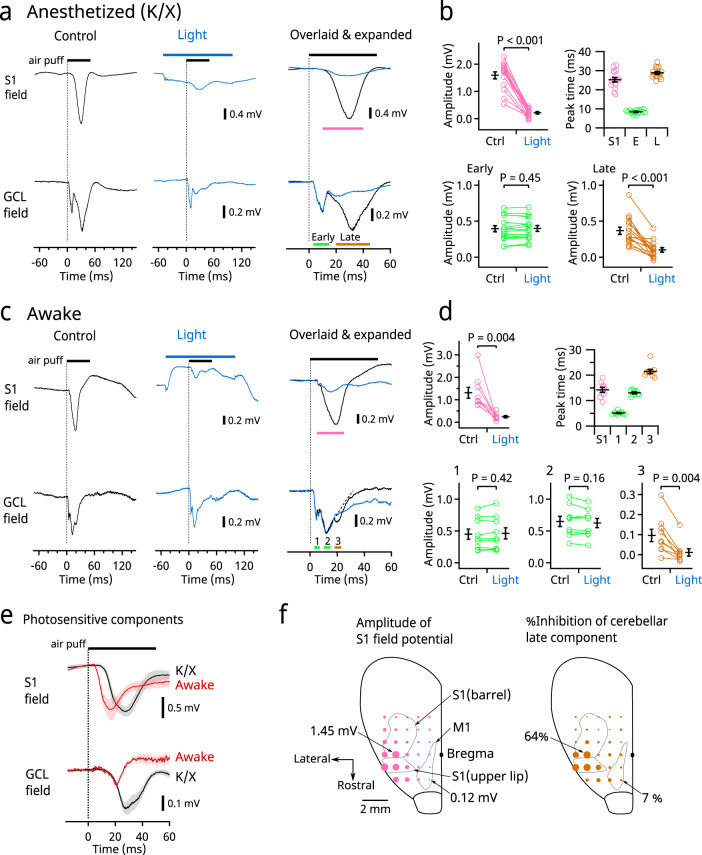
Fig. 2. Optogenetic inhibition of S1 suppresses the late component of the cerebellar sensory response in field potential recordings.
a Representative recordings from a mouse anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine (K/X); 20 traces for each condition were averaged. The same traces are baseline adjusted and overlaid in an expanded time scale in the panels on the right. Black and blue bars indicate the durations of air puff and LED illumination, respectively. The vertical dotted lines indicate the onset of air puff. b Pooled data from 15 anesthetized mice. Peak amplitudes were measured during the times indicated by colored bars in a. The top right panel shows timing of peaks. c Similar to a except using an awake mouse; 46 traces for each condition were averaged. The decay time course of the second component of the cerebellar response was fitted and extrapolated by a single exponential curve (the dashed line) in the panel on the right. d Similar to b except using nine awake mice. The cerebellar late component was measured after subtracting the decay component of the early response (see “Methods” section). e Photosensitive components obtained as differences between the control and the light conditions in K/X (n = 15) and awake (n = 9) mice. Shading indicates SEMs. f Left, bubble size is proportional to the field potential amplitude at each spot measured in the right cerebral hemisphere. Right, bubble size is proportional to the magnitude of inhibition of the cerebellar late component when blue light was applied to each spot. These two values significantly correlated (P < 0.001, n = 29 spots). The cerebellar early component was not affected by photoinhibition at any of these spots. Data from 15 animals under K/X were combined. Each spot is the average from 3–15 animals. S1 for upper lip and barrel and the primary motor cortex (M1) are illustrated in accordance with Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and Mohajerani et al.72. Means ± SEMs are presented as black bars and lines, respectively.