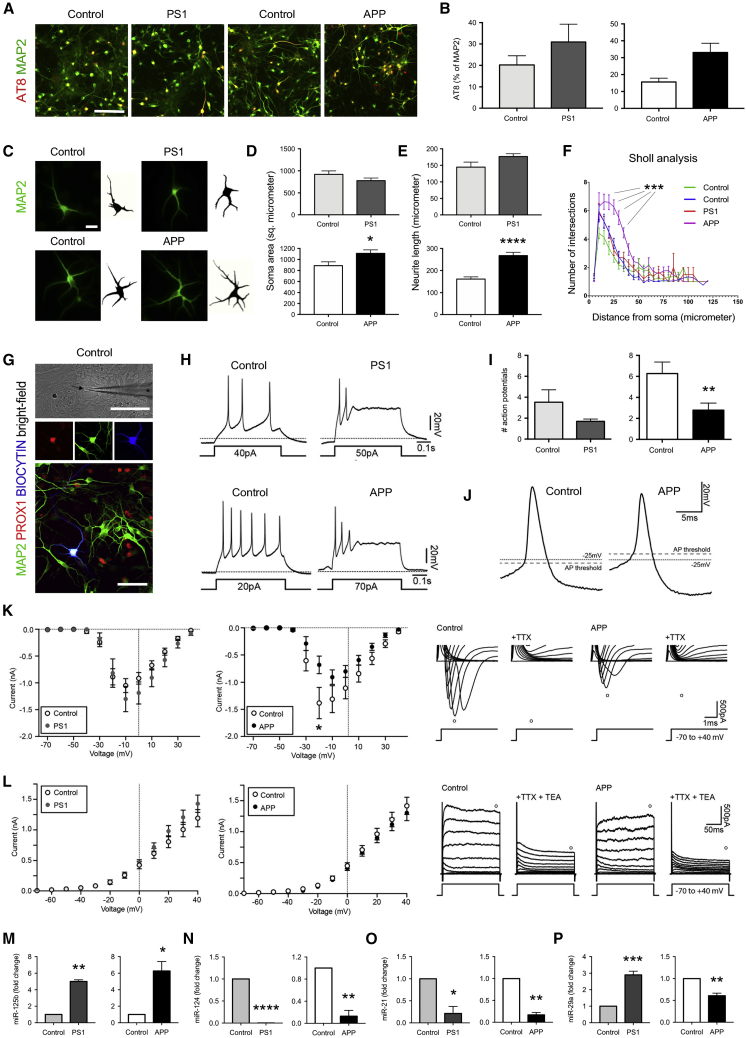
Figure 3.
APP Variant Hippocampal Neurons Exhibit Significant Alterations
(A and B) Characterization of phosphorylation of tau protein in APP variant, PS1 variant, and gender-matched control hippocampal neurons. Immunostaining for phosphorylated tau protein in hippocampal neurons at DIV 56 (A). Quantification of phosphorylated (AT8-positive) neurons expressed relative to the total number of MAP2-positive neurons in hippocampal neurons at DIV 56 (B). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 1–3 independent differentiations per clone for N = 3 iPSC clones per genotype. ∗p < 0.05. Statistical analysis by two-tailed t test. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(C–F) Representative original fluorescence and converted binary images of APP variant, PS1 variant, and gender-matched control MAP2-positive hippocampal neurons at DIV 56 (C). Soma area (D), neurite length (E), and dendritic arborization (F) were quantified. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 16–23 cells per line measured from 3 independent differentiations per genotype. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Statistical analysis by two-tailed t test (D and E) and repeated measures ANOVA (F). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(G–L) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from APP variant, PS1 variant, and gender-matched control hippocampal neurons at DIV 56–58. Representative bright-field image of a patched control cell (arrow) along with the patch-clamp pipette (∗) (G, upper panel) and fluorescence image of a patched PROX1-positive neuron filled with biocytin (G, lower panel). Voltage traces show the ability of hippocampal neurons to fire action potentials (APs) upon current injections (H). Bar diagrams show the maximal number of APs generated upon current injections (I). Expanded voltage traces of the first AP induced by a current ramp of 300 pA and used for determining the AP characteristics (J). Expanded current traces illustrating the inward sodium current (denoted by O) activated during voltage steps ranging from −70 to +40 mV in 10-mV steps (K, right panel). The sodium current was blocked by the presence of 1 μM TTX. The current-voltage plots illustrate the sodium current peak plotted against the voltage steps (K, left panel). Current traces illustrating the outward potassium current (denoted by O) activated during voltage steps ranging from −70 to +40 mV in 10-mV steps (L, right panel). The potassium current was inhibited by the addition of 10 mM TEA. The current-voltage plots illustrate the potassium current plotted against the voltage steps (L, left panel). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 23–26 cells recorded from 3 independent differentiations per genotype. ∗p < 0.05. Statistical analysis by Mann-Whitney test (I) and multiple t tests (K and L). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(M–P) Characterization of microRNA expression in APP variant, PS1 variant, and control hippocampal neurons. Bar diagrams showing the relative expression of miR-125b (M), miR-124 (N), miR-21 (O), and miR-29a (P) measured with RT-PCR in hippocampal neurons at DIV 56. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 3 independent differentiations per genotype. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01. Statistical analysis by two-tailed t test.