Figure 1.
Authentication of the Rainbow hiPSC Model
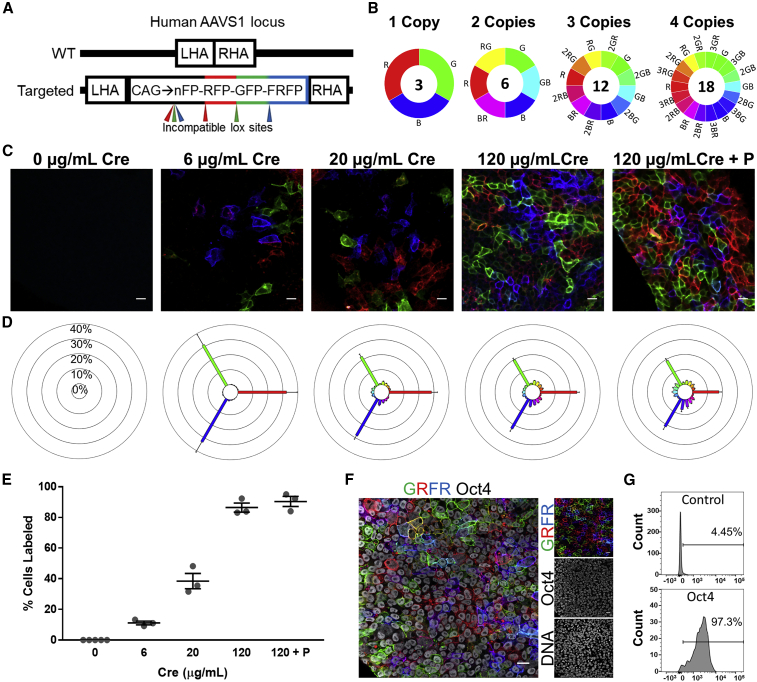
(A) Schematic of the human AAVS1 safe harbor locus depicting the wild-type allele with left homology arm (LHA) and right homology arm (RHA) (top) and targeted, knockedin rainbow cassette containing GFP, RFP, and FRFP flanked by incompatible lox sites for Cre-mediated recombination (bottom).
(B) The number of unique hues possible for a given number of copies of the rainbow cassette. Recombination outcomes that result in the same hue, i.e., recombination of one cassette that expresses RFP versus two cassettes that both express RFP, were considered one unique hue.
(C) Representative confocal images of rainbow hiPSCs that were treated with various doses of Cre and imaged using white light laser and spectral detector settings that prevented spectral bleed-through of the fluorescent proteins. Cells were imaged 72 h after Cre treatment (0–120 μg/mL), or after more than eight passages (120 μg/mL + P). Scale bars, 20 μm.
(D) Spectral analysis of the percentage distribution of hues from the various Cre doses.
(E) Proportion of cells expressing at least one fluorescent protein with varying Cre doses.
(F) Native rainbow fluorescence and immunofluorescence imaging of Oct4. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(G) Representative trace of flow cytometry analysis of Oct4+ rainbow hiPSCs, controls were treated equally but without addition of primary antibody to Oct4.