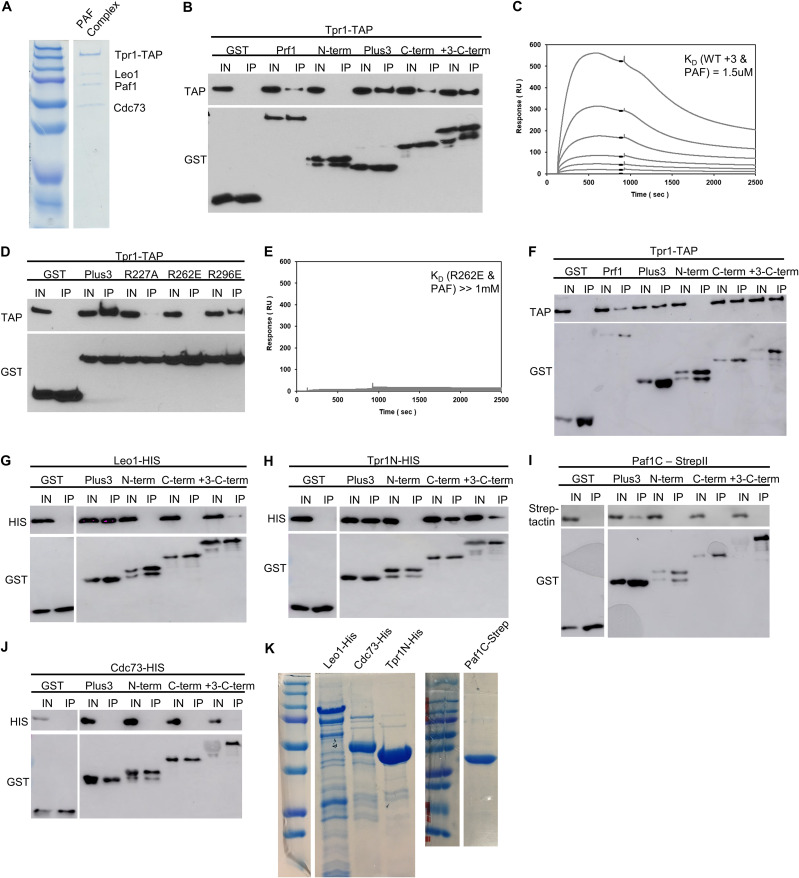
FIG 11.
Prf1 interacts with the PAF complex through its Plus3 domain and C-terminal region. (A) The native PAF complex purified from a tpr1-TAP strain was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. Subunits of the complex are labeled on the right; size markers are indicated on the left. “Tpr1-CBP” refers to Tpr1 fused to the calmodulin-binding peptide that is present after TAP purification. (B) GST pulldown of the native PAF complex (purified via Tpr1-TAP) with full-length, recombinant GST-Prf1 or the indicated domains tagged with GST was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (left). (C) Representative SPR sensorgrams displaying a 2-fold serial titration (0 to 540 nM) of either the wild-type Plus3 domain or the immobilized PAF complex (925 RU). Steady-state binding responses (black bars) were plotted against the concentration to determine the apparent equilibrium dissociation constant (KD). (D) Same as panel B, with the indicated GST-Plus3 domain fusions. (E) Same as panel C, with the GST-R262E mutant. (F) GST pulldown assays of the native PAF complex (Tpr1-TAP) with the full-length protein in the presence of ethidium bromide (0.1%). Recombinant GST-Prf1 or the indicated domains tagged with GST were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (G to J) GST pulldown containing recombinantly expressed subunits of the PAF complex tagged with either 6×His or Strep-tag II and GST-tagged Prf1 fusions. “Paf1C” denotes the C-terminal half of the Paf1 subunit (Paf1C-Strep). “Tpr1N” denotes the N-terminal half of the Tpr1 subunit. Immunoblotting was performed with Strep-Tactin–HRP or the indicated antibodies. For panels B, D, and F to J, “+3-C-term” denotes a fragment of Prf1 consisting of both the Plus3 domain and the C terminus. “I” denotes the input (5%); “IP” denotes the bound fraction (50%). All experiments were repeated at least 3 independent times, and representative blots are shown. (K) SDS-PAGE/Coomassie staining of recombinant PAF complex subunits.