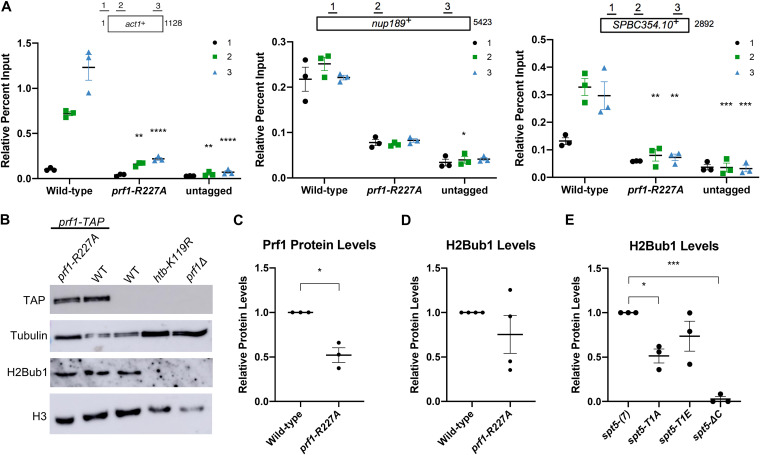
FIG 2.
The prf1-R227A mutation abolishes chromatin association but preserves Prf1 function. (A) TAP tag ChIP was performed on the indicated strains and quantified by qPCR using the indicated primers in act1+, nup189+, and spb354+. Percent IP values were normalized using a primer pair in the S. cerevisiae PMA1 gene. The length of the gene (in base pairs) and positions of PCR amplicons are shown in the diagram at the top. Error bars denote standard errors of the means from 3 independent experiments. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted followed by two-sided t tests with Bonferroni correction between each strain and the wild type within a specific primer pair. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001. (B) Immunoblots of whole-cell extracts from the indicated strains. Controls on each blot are the wild-type (WT) prf1-TAP strain (left) and an untagged strain (right). Antibodies are indicated on the left. (C) Quantification of immunoblots analyzing Prf1-TAP protein levels normalized to tubulin and then the wild type for the prf1-R227A strain. (D) Quantification of H2Bub1 levels normalized to total H3 levels and then the wild type for the prf1-R227A strain. (E) Quantifications of H2Bub1 levels normalized to total H3 levels in spt5 mutant strains. spt5(7) levels were set to 1. For panels C to E, error bars denote standard errors of the means from 3 independent experiments. A one-sample two-sided t test was conducted between each strain and its relative normalized wild type. *, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001.