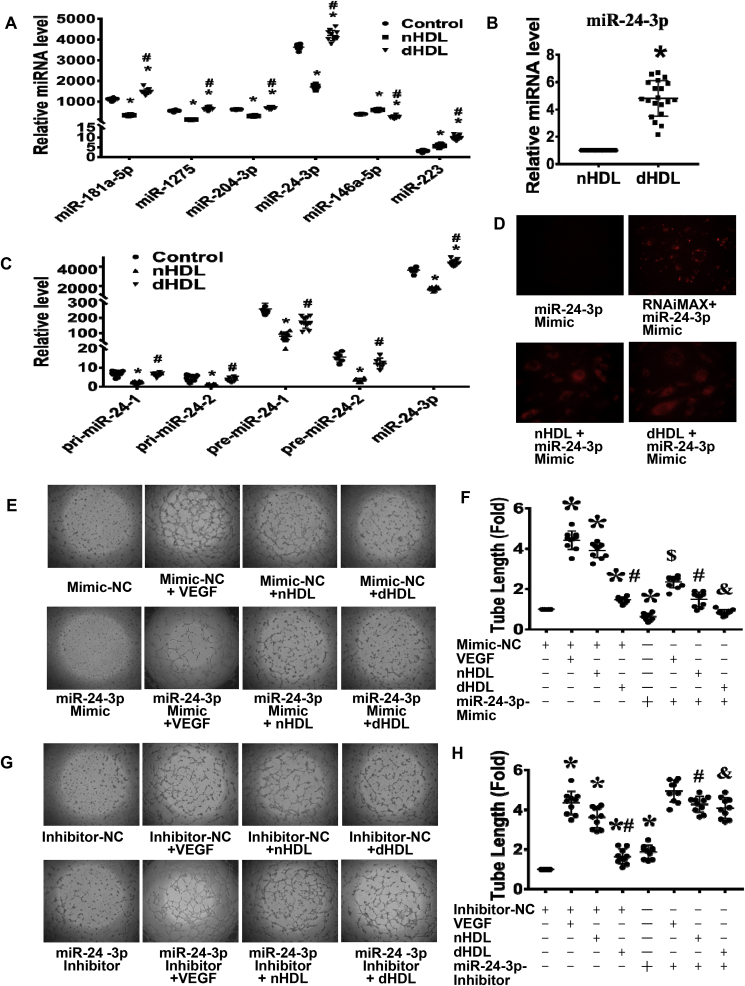
Fig. 2.
MiRNA microarray revealed that nHDL suppressed, but dHDL enhanced expression of miR-24-3p in endothelial cells (ECs), which affected tube formation.(A) The qRT-PCR confirmed that four miRNAs were downregulated, whereas one miRNA was upregulated by nHDL. In contrast, these four miRNAs were upregulated, whereas miR-146a-5p was downregulated by dHDL. dHDL increase miR-223 more than nHDL, but the levels of miR-223 in ECs is hundred folds less than other miRNAs * vs. control; # vs. nHDL, p < 0.05 (n = 8–10). (B) The level of miR-24-3p was higher in dHDL than in nHDL. *p < 0.05 (n = 20). (C) The nHDL inhibited, but dHDL slightly decreased, the expressions of pri-miR-24-1, pri-miR-24-2, pre-miR-24-1 and pre-miR-24-2 in cultured ECs. * vs. control; # vs. nHDL, p < 0.05 (n = 6–10). (D) The image showed that miR-24-3p mimic alone can not enter into ECs, but Lipofectamine® RNAiMAX, nHDL and dHDL can deliver Cy3-labeled miR-24-3p mimic to ECs. (E–H) The miR-24-3p mimic inhibited EC tube formation, whereas the miR-24-3p inhibitor enhanced EC tube formation. The miR-24-3p mimic decreased VEGF and nHDL-induced EC tube formation, whereas the miR-24-3p inhibitor increased dHDL-induced EC tube formation. The miR-24-3p inhibitor further enhanced nHDL-induced EC tube formation. NC, negative control, * vs. Mimic-NC or Inhibitor-NC; # vs. Mimic-NC + nHDL or Inhibitor-NC + nHDL; & vs. Mimic-NC + dHDL or inhibitor-NC + dHDL, $ vs. Mimic-NC + VEGF, p < 0.05 (n = 10–14).