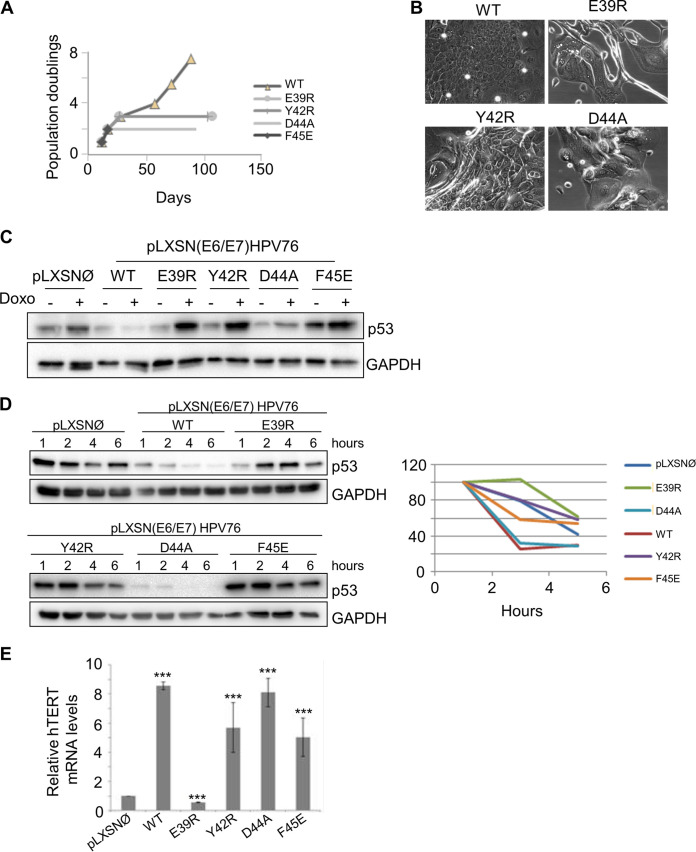
FIG 5.
Mutation of HPV76 E6 in amino acid residues corresponding to p53 and E6AP binding sites in HPV16 E6 altered its biological activities. (A) Growth curve of primary HFKs expressing E6/E7 with WT E6 or mutated E6. PDs are reported on the vertical axis. (B) Morphology of HFKs transduced with the indicated recombinant retroviruses at PD2. The same magnification (×20) was used for all the microphotographs. (C) NIKs transduced with E7 and with WT or mutated E6, or with the empty vector (pLXSNØ) as a control, were treated with the DNA-damaging agent doxorubicin (Doxo) used for 8 h at the final concentration of 10 μg/ml. Levels of p53 and GAPDH were determined by IB using specific antibodies. (D) (Left) NIKs transduced as described in the Fig. 4D legend were treated with a protein synthesis inhibitor (cycloheximide, at the final concentration of 10 μg/ml) and collected at the indicated time points. Twenty micrograms of total protein extracts from NIKs expressing pLXSNØ, WT, and E39R E6 mutant were run on a Western blot separately from NIKs expressing Y42R, D44A, and F45E E6 mutants (upper and lower panels, respectively). Levels of p53 and GAPDH were determined by IB using specific antibodies. (Right) Graph showing quantification of p53 signal, normalized to GAPDH levels and calibrated against the levels of p53 at 2 h of treatment (set as 100%). Results shown are the means of data from 3 independent experiments. (E) Total RNA was extracted from the indicated NIKs and retrotranscribed. hTERT gene expression was determined by quantitative PCR and normalized to GAPDH. The histogram represents the quantification of the results from three independent experiments. ***, P < 0.005.