Figure 1.
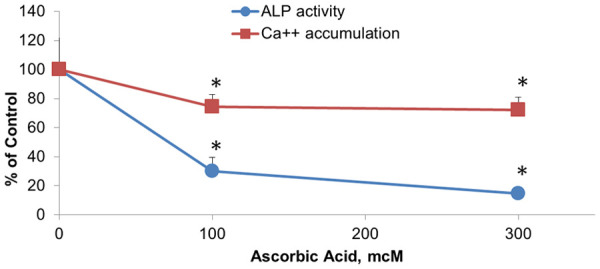
Effects of ascorbic acid on calcification of extracellular matrix in cultured human aortic smooth muscle cells (AoSMC). Human AoSMC were seeded in 96 well plates and grown to confluency in 5% FBS/DMEM. Cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of ascorbic acid for four days in cell growth medium. Cell associated alkaline phosphatase activity was evaluated by accumulation of fluorescent product (360 nm exitation/450 nm emmission) after cell incubation with 25 mcg/ml 4-MUP (fluorescent ALP substrate, Sigma) in alkaline buffer (Sigma)/1% Triton X100 for 1 h at room temperature. In separate plate cell layers were washed with PBS and extracellular matrix (ECM) was exposed by cell removal with NH4OH/Triton X100 treatment. Calcium from ECM was solubilized by incubation in 0.6 N HCl for 48 hours at 37°C. Calcium content in solubilized samples was measured with Calcium diagnostic kit (TECO Diagnostics). Results were expressed as percentage of cell samples incubated in plain unsupplemented cell growth medium. *, indicates significant differences from unsupplemented controls (P<0.05) in two-tailed t-test.
