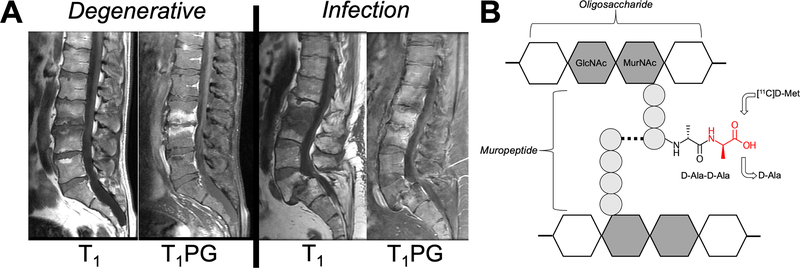
Figure 1.
Approach to image vertebral discitis-osteomyelitis (VDO) via microorganism-specific incorporation of PET-labeled D-amino acids. (A) Variable imaging appearance of VDO via MRI. The MRIs of two patients are shown. T1-weighted imaging with and without contrast show abnormalities of the vertebral end-plates and discs that are similar for VDO and osteoarthritis (degenerative disease). (B) Structure of bacterial peptidoglycan (a high quantity present in S. aureus, the most common pathogen in VDO). The C-terminal D-Ala-D-Ala sequence of peptidoglycan muripeptide is highlighted, as well as the putative site of D-[11C]Met incorporation (red).