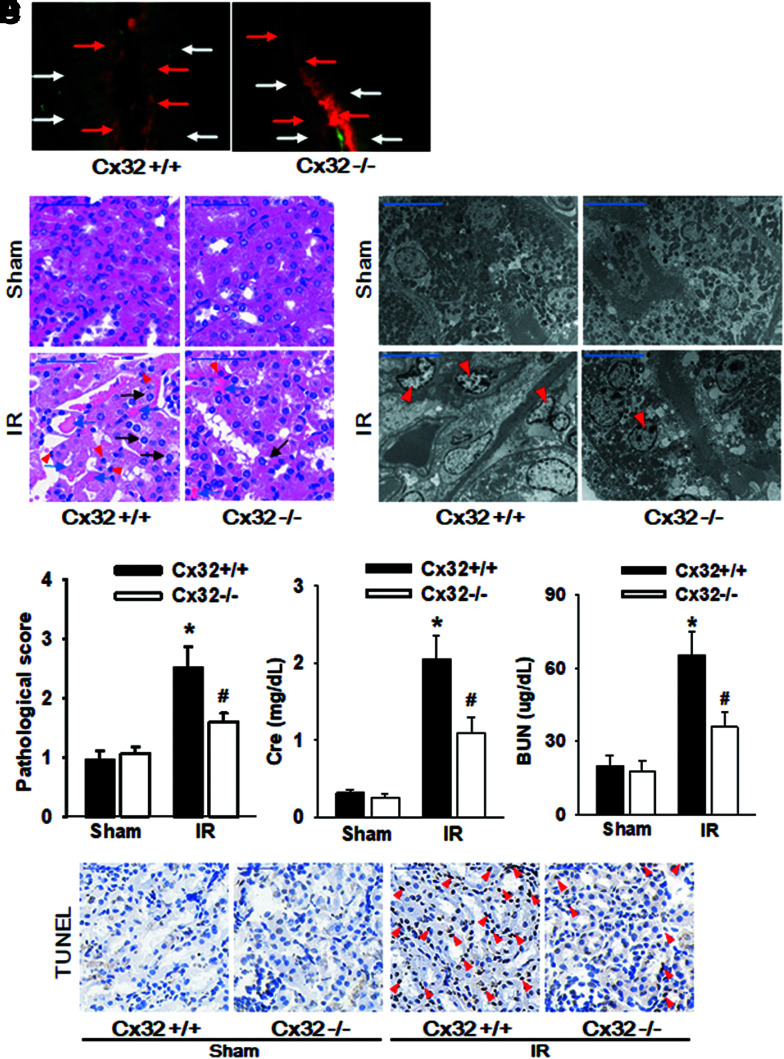
FIG. 2.
Cx32 deficiency protects against IR-induced AKI and renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis. Cx32−/− and Cx32+/+ C57BL/6 mice underwent renal IR were sacrificed at the time point of 24 h after reperfusion. (A) “Scrape-and-load” assay was used to valuate functional GJ in kidney tissue. Function of GJ is demonstrated by the spread of GJ-permeable Lucifer yellow (white arrow), and in contrast Rhodamine is impermeable (red arrow). (B) Renal damage of Cx32−/− and Cx32+/+ C57BL/6 mice after renal IR exposure (H&E; scale bar 50 μm). Blue arrow: tubular necrosis; red arrow: inflammatory cells; black arrow: cell swelling and cytoplasm rarefaction. (C) Ultrastructural mitochondrial injury of Cx32−/− and Cx32+/+ C57BL/6 mice after renal IR exposure (TEM; scale bar 10 μm). Red arrow: cell nuclear condensation. (D) Kidney histopathology evaluation scores, levels of Cr and BUN of Cx32−/− and Cx32+/+ C57BL/6 mice 24 h after renal IR. (E) Renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis of Cx32−/− and Cx32+/+ C57BL/6 mice 24 h after renal IR with TUNEL staining (scale bar 50 μm). Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 8). *p < 0.05 versus Cx32+/+ sham group; #p < 0.05 versus Cx32+/+ IR group in (C). Cx32−/− mice, Cx32-gene knockdown mice; Cx32+/+ mice, wild-type mice; GJ, gap junction; TEM, transmission electron microscopy. Color images are available online.