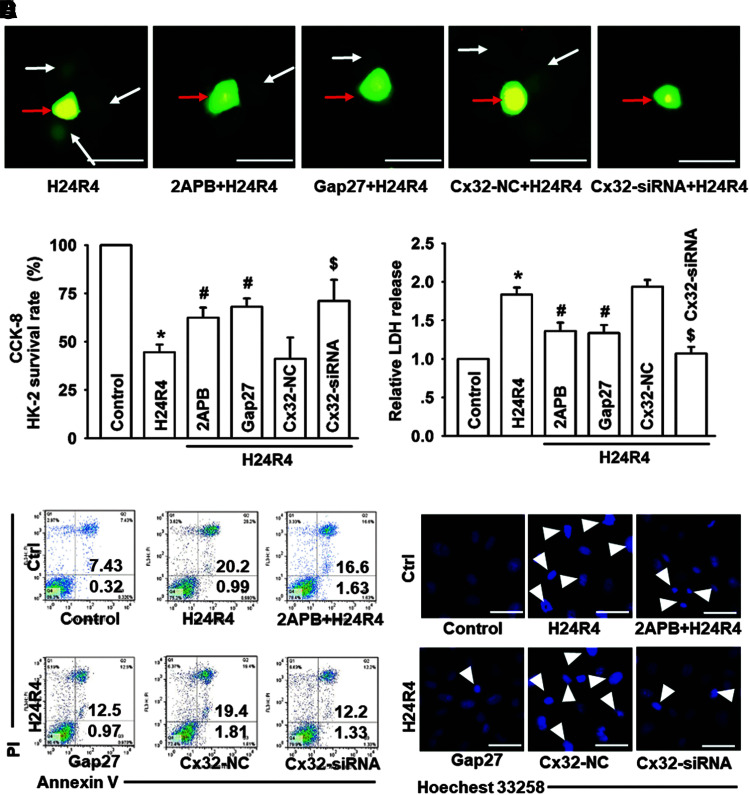
FIG. 5.
Cx32 inhibition attenuated H24R4-induced cell injuries and apoptosis of HK-2 cells. Before H24R4 exposure, different methods were used to inhibit GJ function composed of Cx32 in HK-2 cells, including 2APB (gap junction inhibitor, 25 μM, 1 h pretreatment), Gap27 (Cx32 peptide, 100μM, 24 h pretreatment) and specific Cx32-siRNA, to observe effects of Cx32 GJ function on HK-2 cells damage and apoptosis. (A) “Parachute” dye-coupling assay was used to determine effects of 2-APB, Gap27, and Cx32-siRNA on decreasing GJ function (scale bar 50 μm). Function of GJ is demonstrated by the spread of GJ-permeable calcein-AM (white arrow), and in contrast CM-Dil is impermeable (red arrow). (B, C) Effects of 2APB, Gap27, and Cx32-siRNA on HK-2 cell growth and relative LDH release. (D, E) HK-2 cell apoptotic rates were detected by flow cytometry and Hoechst 33258 staining, as described in the Methods and Materials section. The white arrow (E) pointing the apoptotic nuclei. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 4). *p < 0.05 compared with control group; #p < 0.05 versus H24R4 group. $p < 0.05 compared with Cx32-NC+H24R4 group in (B–D). 2-APB, 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate; H24R4, hypoxia for 24 h and reoxygenation for 4 h; HK-2, human kidney tubular epithelial cell; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase. Color images are available online.