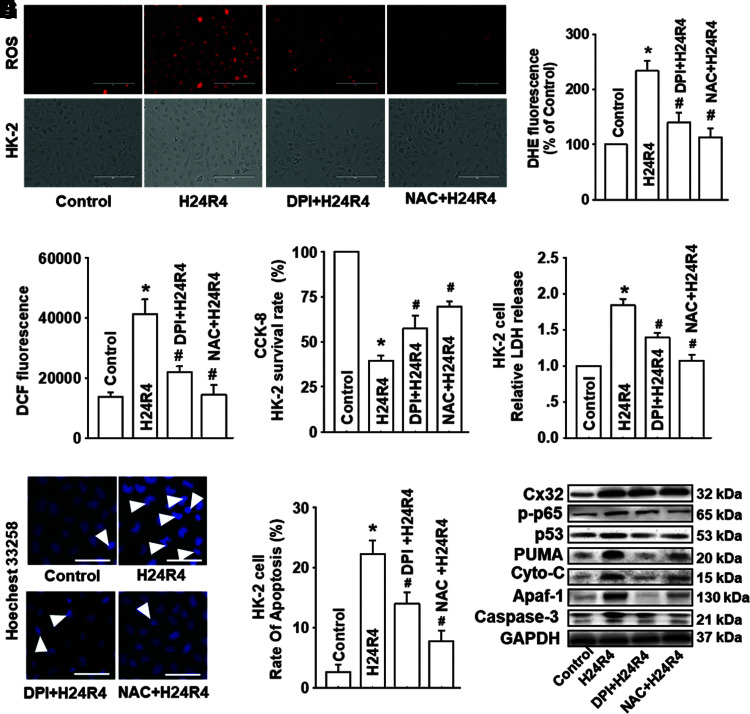
FIG. 7.
Inhibitors of ROS, DPI, and NAC attenuated the activation of NF-κB/p53/PUMA-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis effectively, but had no influence on the expression of Cx32. Before H24R4 exposure, DPI (an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase, 1 μM, 1 h pretreatment) and NAC (a ROS scavenger, 10 mM, 1 h pretreatment) were used to alter ROS generation and distribution, to observe effects of ROS on HK-2 cells damage and apoptosis, and even on expression alternation of mitochondrial apoptosis-related proteins. (A–C) Effects of DPI and NAC on HK-2 cellular ROS production after H24R4 exposure, detected with DHE staining (A, B, stained in red, scale bar 50 μm) and DCFH-DA staining (C). (D, E) Effects of DPI and NAC on HK-2 cell growth and relative LDH release after H24R4 exposure. (F, G) Effects of DPI and NAC on H24R4-induced HK-2 cell apoptosis, detected with Hoechst 33258 staining (F, white arrow: apoptotic nuclei, scale bar 50 μm) and flow cytometry (G). (H) DPI and NAC application attenuated expression of p-p65, p53, PUMA, cytochrome-C, Apaf-1, and caspase-3 after H24R4 exposure, but had no significant influence on Cx32 expression. Western blotting analysis was conducted. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 4). *p < 0.05 compared with control group; #p < 0.05 versus H24R4 group. NAC, N-acetyl cysteine. Color images are available online.