Figure 1.
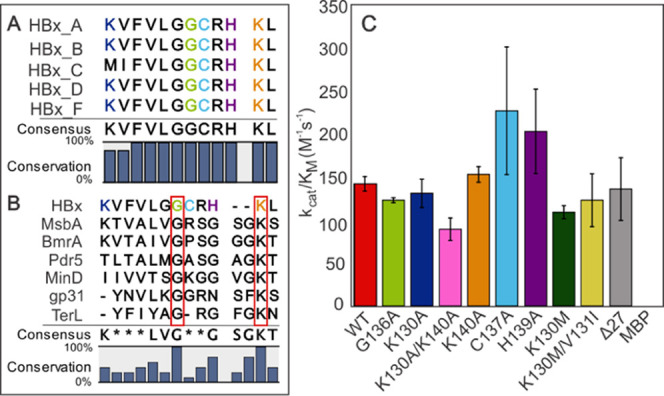
Predicted nucleotide-binding domain and ATP hydrolysis by WT and variant MBP-HBx. (A) Sequence alignment of the predicted HBx nucleotide-binding region in the well-studied HBx genotypes. Residues thought to be important for binding and/or are known to be essential for the HBx function are shown in colors. (B) Sequence alignment of the HBx (A2) putative ATP-binding domain and known Walker A motifs. MsbA, Pdr5, and BmrA contain canonical Walker A sequences, while MinD, gp31, and TerL utilize Deviant I, Deviant II, and Deviant III Walker A motifs, respectively. The red boxes highlight the residues conserved in all sequences. (C) Catalytic efficiency of MBP-HBx WT and variants of the putative ATP-binding domain. Error bars represent standard error. Error bars for MBP are not visible due to the y-axis scale.
