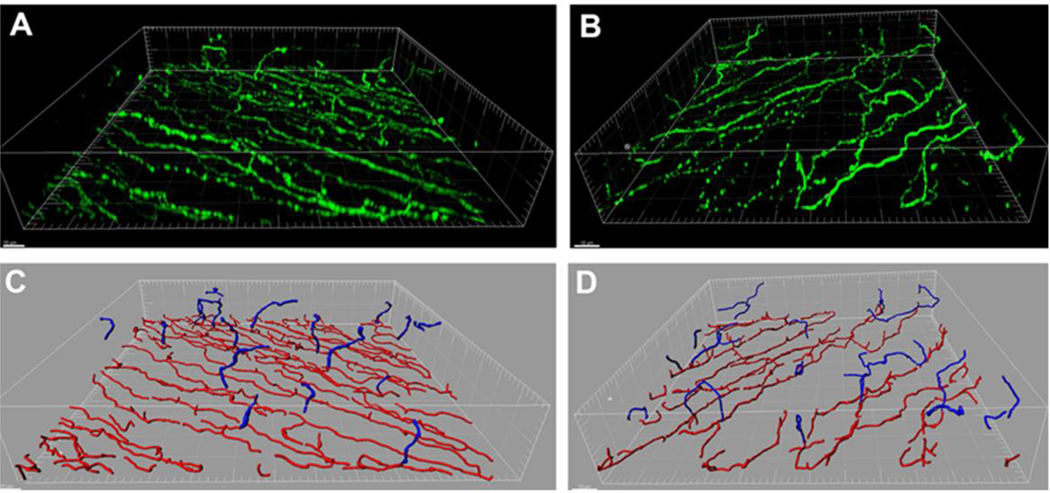
Figure 4:
Epithelial thinning is associated with loss of the subbasal nerve plexus in a Type 1 streptozotocin diabetic mouse model. (A) Three-dimensional surface rendering of the subbasal nerve plexus and associated terminal epithelial nerves in a control mouse. β-tubulin III staining in green. (B) Three-dimensional surface rendering of a Type 1 diabetic mouse. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C – D) Nerve modeling and segmentation using IMARIS Filament. Representative images showing the subbasal nerve plexus is shown in red, terminal epithelial nerves in blue (C, normal; D diabetic). Scale bar: 10 μm. Loss of the subbasal nerve plexus in (D) was associated with significant thinning of the corneal epithelium after 12 weeks of diabetes, 34.0 μm ± 3.0 μm (diabetes) compared to 38.6 μm ± 3.8 μm (control). Figure taken from Cai et al. Am J Pathol 2014.