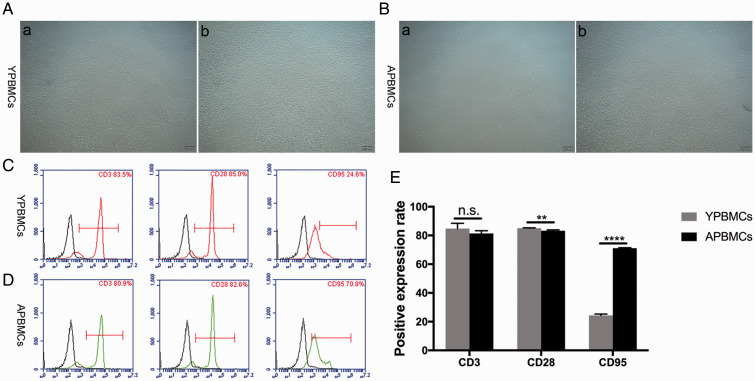
Figure 2.
Extraction, culture, and identification of PBMCs from donors of different ages. (A): (a) PBMCs isolated from younger donors, (b) PHA-activated PBMCs from younger donors (scale bar: 200 μm). (B): (a) PBMCs isolated from older donors, (b) PHA-activated PBMCs from older donors (scale bar: 200 μm). (C): Analysis of CD3, CD28, and CD95 surface markers in PBMCs from younger donors. (D): Analysis of CD3, CD28, and CD95 surface markers in PBMCs from older donors. (E): Rate of CD28 expression decreased with age and rate of CD95 expression increased with age. Data represent three independent experiments. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (**p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, n.s., no significance).
Abbreviations: CD, cluster of differentiation; hPDLSCs, human periodontal ligament stem cells; OPBMCs, older peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PHA, phytohemagglutinin; YPBMCs, younger peripheral blood mononuclear cells.