Figure 1.
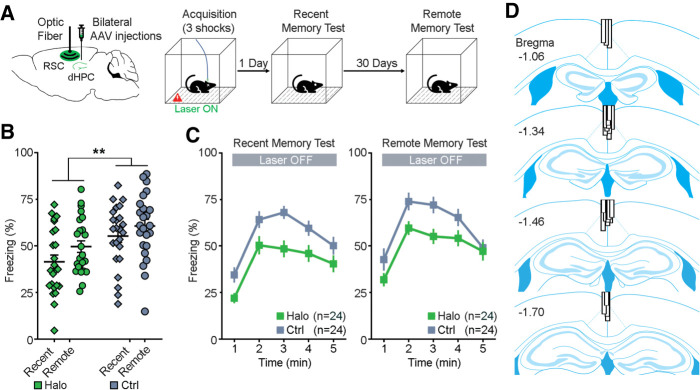
Optogenetic inhibition of dHPC-to-RSC pathway during memory acquisition. (A) Schematic drawing (left) of bilateral injections of AAV viruses that encode either halorhodopsin (Halo) or YFP (Ctrl) into the dHPC and an optical fiber implant into the RSC. Contextual fear conditioning procedure (right). Mice received optogenetic inhibition of the dHPC-to-RSC neuronal terminals during acquisition of memory on day 0. Then mice were tested for recent memory on day 1 and remote memory on day 31, receiving no laser stimulation. (B) Percentage of freezing (mean of 5 min) during the recent memory test (day 1) and remote memory test (day 31). (**) P = 0.004, repeated measures ANOVA between groups. (C) Minute-by-minute percentage of freezing from B of recent (left) and remote (right) memory tests. Both left and right, P < 0.05; Bonferroni post-hoc of the means between Halo/Ctrl. All error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM). (D) Optical fiber placements of the Halo group were confirmed mostly dorsal to the RSC, arranged anterior (top) to posterior (bottom). Adapted from Franklin and Paxinos 2008.