Figure 2.
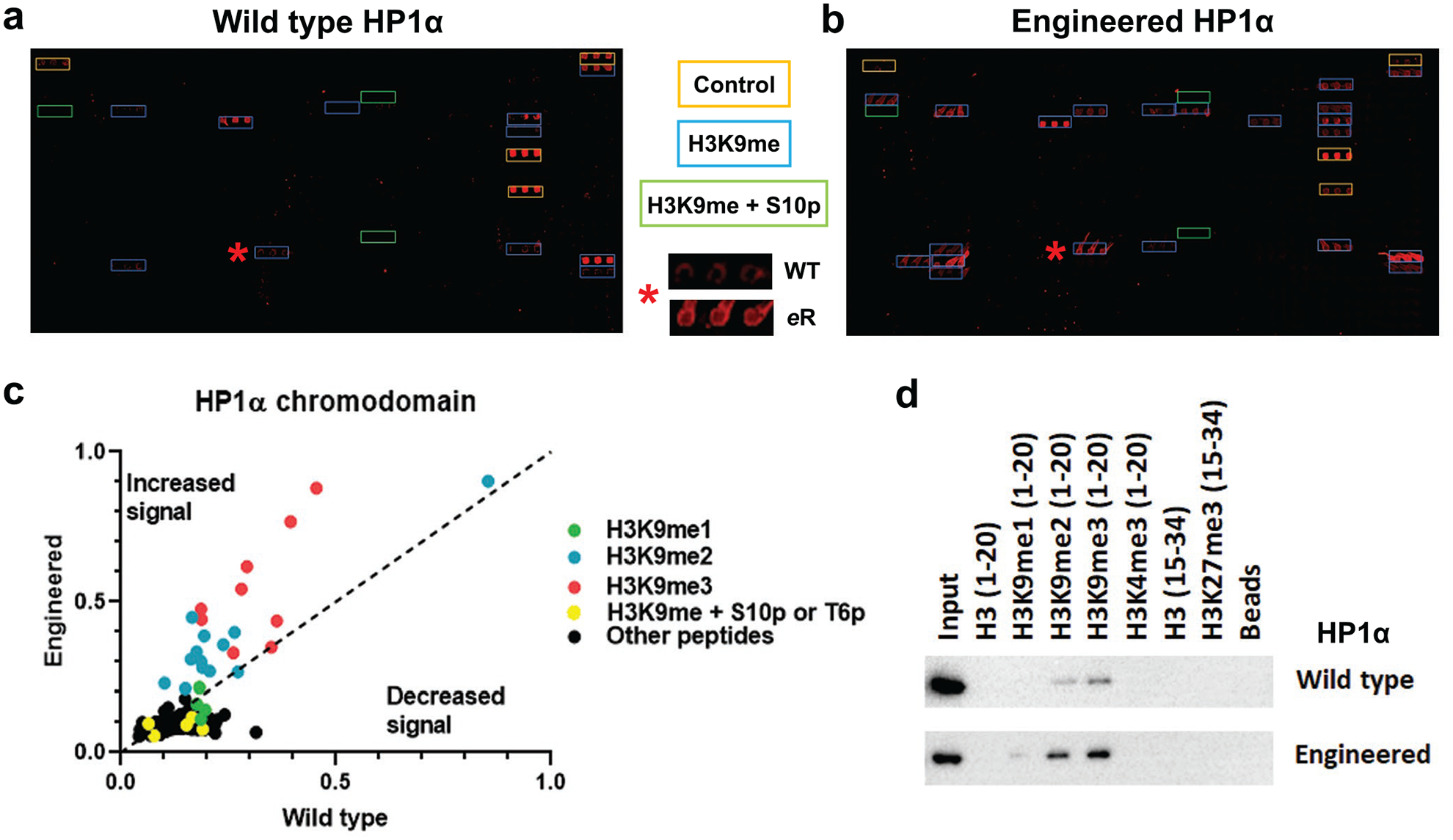
Mutation of the HP1α chromodomain increases binding to H3K9 methylation. a) and b) Images of histone peptide microarrays probed with either MBP-tagged wild-type (a) or engineered (b) HP1α chromodomain. Color coded boxes indicate peptide types and positive controls (IgG). The red star indicates a peptide (H3K9me3 containing) hit that has been zoomed in on (center panel), highlighting the change in binding between the two constructs. c) Scatter plot of the array data for HP1α chromodomains, scaled from 0–1 (further detail in Methods) and the indicated types of peptides color coded, where peptides with increased signal for the engineered protein fall above the dashed line and those with weaker signal below it. d) Western blot for peptide pulldowns of the wild-type and engineered HP1α proteins using peptides containing the known target sequences and potential off-targets for chromodomains. All arrays were performed using 500 nM of protein and all pulldowns with 5 pmol protein. All images and data are representative of n ≥ 3 experiments (subarrays or pulldowns).
