Figure 5.
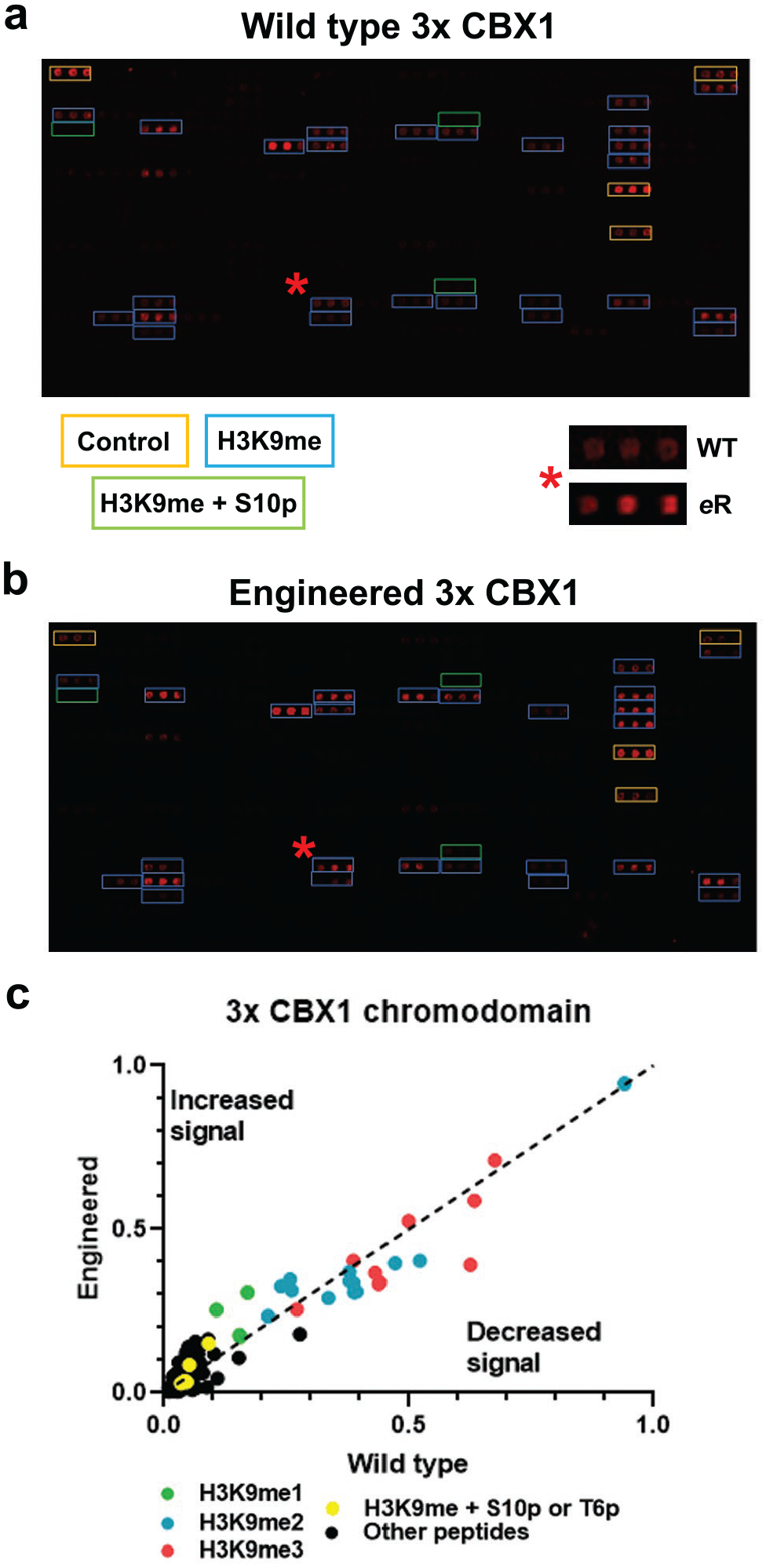
Multimerization of CBX1 wild-type and engineered chromodomains show similar binding to H3K9 methylated peptides. a) and b) Images of histone peptide microarrays probed with either MBP-tagged wild-type (a) or engineered (b) triple CBX1 chromodomains. The red star indicates a peptide (H3K9me3 containing) hit that has been zoomed in on to the right represents the change in binding between the two constructs. c) Graph of the triple reader domains with the engineered domain plotted against the wild-type construct so that enhanced signal for the mutant construct is above the dashed line and decreased signal is below the line; peptides with the specified modifications are color coded as indicated. All arrays were performed using 500 nM of protein. All images and data are representative of n ≥ 3 experiments.
