Table 6.
Comparison of CLARITY-BPA study design with prior academic studies. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this table legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
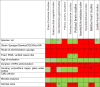 |
Red color indicates that aspect of the published independent studies was different from that of the CLARITY-BPA study design. For example, no published independent studies used the Sprague-Dawley/CD23/Nctr BR, the CMC vehicle.
Green color indicates that aspect of the published independent studies was similar to that of the CLARITY-BPA study design. For example, all published independent studies analyzed their results blinded, as did the CLARITY-BPA study.
The numbers explain some subtle differences between the published independent studies and the CLARITY-BPA study.
1. Mice and rats used.
2. No prior studies have used gavage, although many have used oral exposure routes.
3. Sprague Dawley from Zivic Miller.
4. Sprague Dawley, Holzman.
5. Small number of prior studies have examined rat mammary glands (Wistar/Furth and Sprague Dawley), but more data from the Soto lab has come from mouse models.
6. BPA administered via diet.
7. Diet used in some studies; other diets also used.
8. No studies dosed pups directly.
9. For studies in the Rosenfeld laboratory, females were exposed 2 weeks before gestation and throughout the postnatal period to replicate real-world exposure.
10. Polypropylene cages and glass water bottles.
11. Animals in the Rosenfeld laboratory were housed in polypropylene or polystyrene cages.
12. Polyethylene cages and water bottles.
13. Sample size in CLARITY-BPA less than requested.
14. Variable sample sizes, some larger than CLARITY-BPA.
