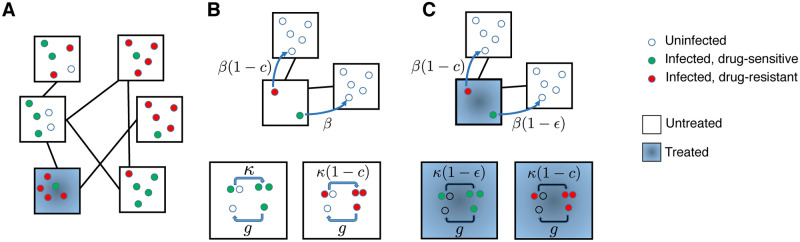
Fig 2. A structured population model for the spread of drug-resistant and drug-sensitive strains of an infection.
A) An example population, divided into six equal subpopulations (“demes”, black squares) of five individuals (circles). Infection can spread within demes, and also between demes that are connected (black lines). Individuals are categorized based on their infection status (uninfected: open circle, infected with drug-sensitive strain: green circle, infected with drug-resistant strain: red circle). The deme where an individual is located may determine whether or not they will receive drug treatment (blue shading), or more generally, their probability of receiving treatment. B) Untreated deme: The wild-type strain (green) is transmitted at rate κ within a deme (bottom) and rate β between demes (top). Individuals infected with any strain recover with a rate g. The resistant strain (red) pays a cost c in its transmission rate with or without drug. C) Drug-treated deme: Transmission of the resistant strain is unaffected by whether the source individual is receiving treatment, but transmission of the wild-type strain (green) both within (bottom) and between (top) demes is reduced by a factor (1 − ϵ) if the source individual is treated, where ϵ is the drug efficacy.