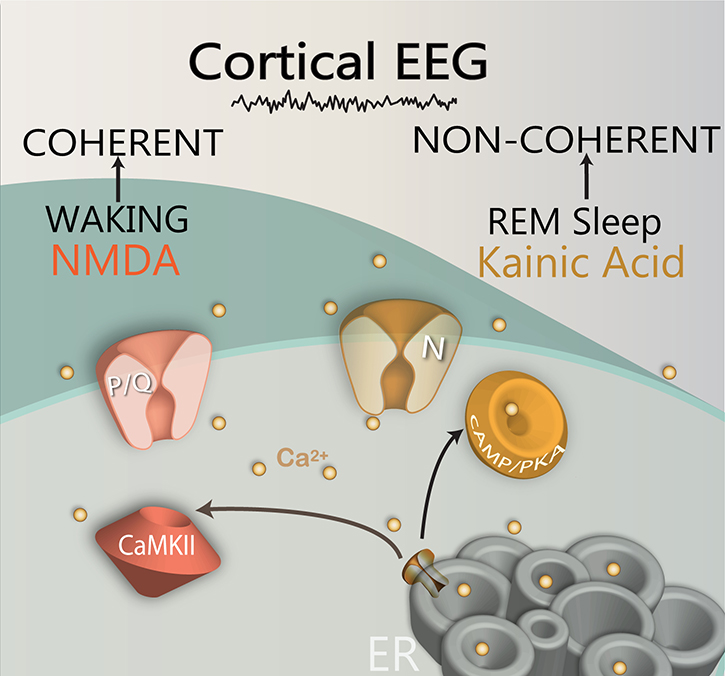
Figure 4. Differential regulation of two calcium channels by different intracellular pathways.
The CaMKII (brown structure) intracellular pathway regulates P/Q-type calcium channels, while the cAMP/PKA (orange structure) pathway regulates N-type calcium channels. The CaMKII/P/Q-type channel pathway modulates beta/gamma band activity during waking, while the cAMP/PKA/N-type channel pathway modulates beta/gamma band activity during REM sleep. In addition, NMDA receptor activation modulates P/Q-type channel activity, while kainic acid receptor activation modulates N-type channel activity. The gamma band oscillations generated by the PPN during waking ultimately lead to gamma activity in the cortical EEG with coherence across distant sites, while gamma activity during REM sleep leads to a similar fast cortical EEG but without coherence across distant sites. (Ca2+, light brown dots)