Figure 2. Mechanism of inhibition of protein ER import and maturation, and location of common resistance mutations within the structure of the Sec61 protein translocon.
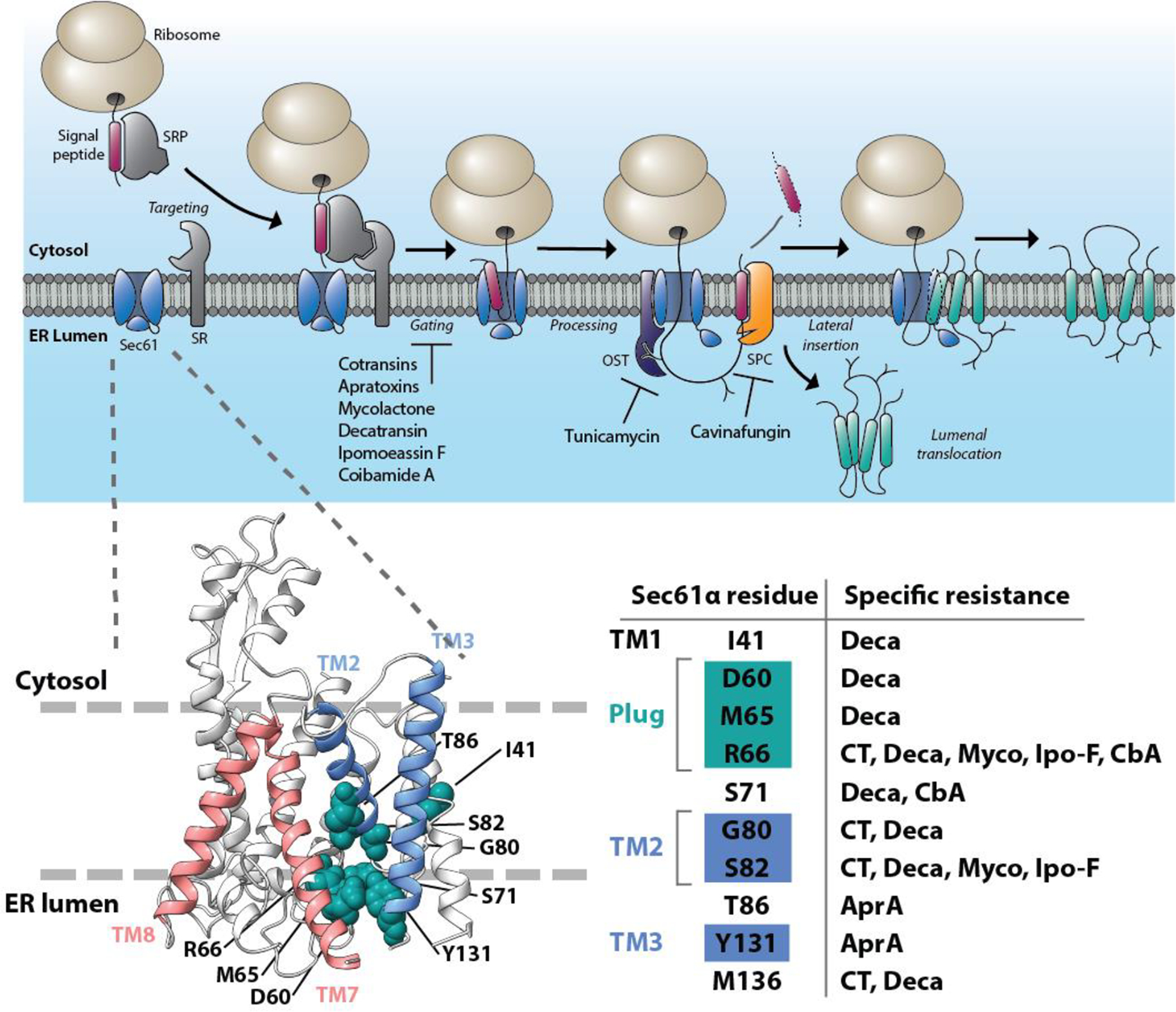
The pathway of cotranslational mammalian protein import into the ER (top). Inhibitors of Sec61 protein translocon prevent channel gating and insertion of secreted proteins into the ER lumen or diffusion of integral membrane proteins into the ER lipid bilayer. Tunicamycin is an inhibitor of cotranslational protein N-glycosylation, whereas cavinafungin prevents ER targeting signal peptide cleavage. In the structural model of mammalian Sec61 (bottom), the lateral gate helices of Sec61 are indicated in blue (TM2 and TM3) and red (TM7 and TM8) and the resistance mutations identified to confer strong resistance to most structurally diverse Sec61 inhibitors are shown in green and outline the putative NP-binding site on the lumenal end of the Sec61 lateral gate. SRP, Signal Recognition Particle. OST, Oligosaccharyl transferase complex. SPC, signal peptidase complex. CT, cotransin; Deca, decatransin; Myco, mycolactone; Ipo-F, ipomoeassin F; AprA, apratoxin A.
