Figure 7.
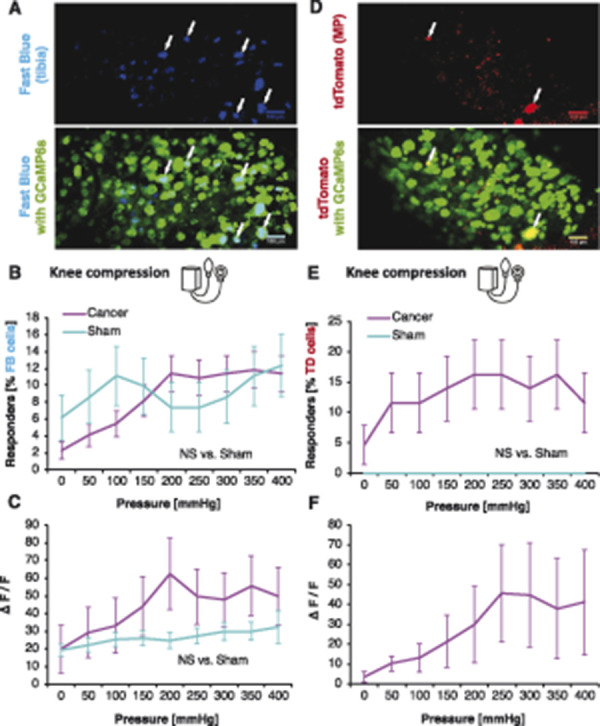
Intratibial and peritibial afferent function in health and bone cancer. Fast Blue (FB)-traced neurons from the tibial cavity. Representative z-stack collected at the end of the in vivo imaging experiment to identify traced cells (blue) and GCaMP6s (green). Scale bars: 100 µm. Arrows indicate FB-traced neurons (A). Percentage of responders of all FB-traced tibial afferents within L3 and L4 DRG during knee compression in sham and CIBP rats. Data represent the mean ± SEM of n = 81 cells from 6 animals (sham) and 220 cells from 9 animals (cancer). Repeated-measures ANOVA: NS, nonsignificant (B). Fluorescence intensities of all responding FB+ neuronal cell bodies to knee compression. Pressure was increased in 50-mm Hg increments every 10 seconds. Data represent the mean ± SEM of n = 15 cells (sham) from 6 animals, and n = 34 cells from 9 animals (CIBP). Repeated-measures ANOVA: NS, nonsignificant (C). AAVrg/tdTomato (TD)-traced neurons innervating the muscle and periosteum (MP) surrounding tibia. Representative z-stack collected at the end of the in vivo imaging experiment to identify traced cells (red) and GCaMP6s (green). Scale bars: 100 µm. Arrows indicate TD-traced neurons (D). Percentage of responders of all TD-traced MP afferents within L3 and L4 DRG during knee compression in sham and cancer animals. Pressure was increased in 50-mm Hg steps every 10 seconds (see methods for more). Data represent the mean ± SEM of n = 14 cells from 3 animals (sham) and 43 cells from 5 animals (cancer). Repeated-measures ANOVA: NS, nonsignificant (E). Fluorescence intensities of all responding TD+ neuronal cell bodies to knee compression. Pressure was increased in 50-mm Hg increments every 10 seconds. Data represent the mean ± SEM of n = 9 cells (cancer) from 3 animals. No between-group comparison was performed because in sham, no cells responded (F). ANOVA, analysis of variance; CIBP, cancer-induced bone pain; DRG, dorsal root ganglia.
