Figure 1.
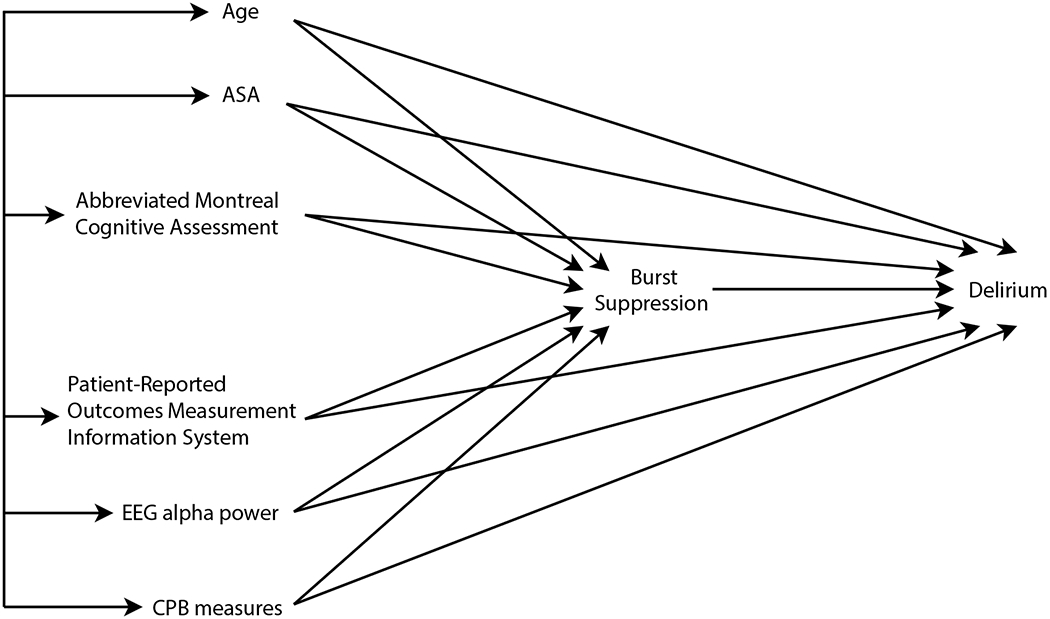
Initial Hypothetical Causal Model. Burst-suppression during cardiopulmonary bypass was hypothesized to mediate the association between known delirium risk factors and delirium. However, the initial model also allowed for the possibility of direct effects of the risk factors on delirium, in addition to, or instead of the indirect, mediational effect of burst-suppression. PROMIS measures included applied cognition, physical function, global health, pain, and sleep. CPB measures included duration of CPB and lowest temperature during CPB. Straight arrows indicate causal effects; double-headed arrows connecting exogenous variables on the left indicate correlations not explicated in the model.
ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status; aMOCA, abbreviated Montreal Cognitive Assessment; PROMIS, Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System; EEG, electroencephalogram; CPB, cardiopulmonary bypass measures
