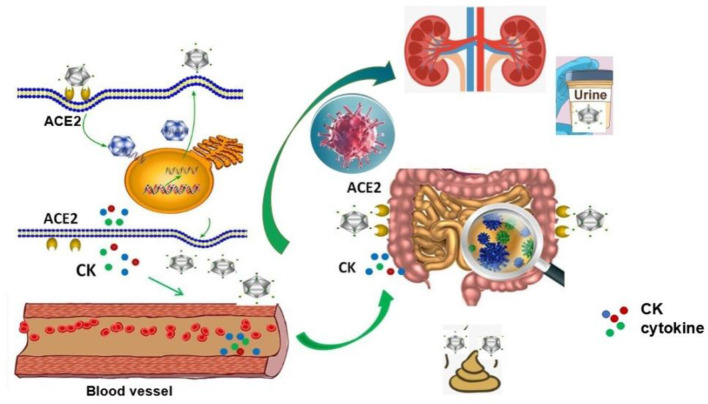
Figure 5.
Possible mechanisms of blood transmission after viral infection. After SARS-CoV-2 enters into the lung from mouth and throat and infects cells, the virus replicates in the cell and releases more new viruses. Massive accumulation of SARS-CoV-2 leads to a surge of immune cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which resulting in a rapid increase in CK levels in the blood, or releasing more virus particles into the blood circulation. The virus and cytokines positively induce high expression of ACE2 in the intestinal epithelium and other organs, which accelerates overexpression of ACE2 and viral binding, causing the systemic infections with the virus.