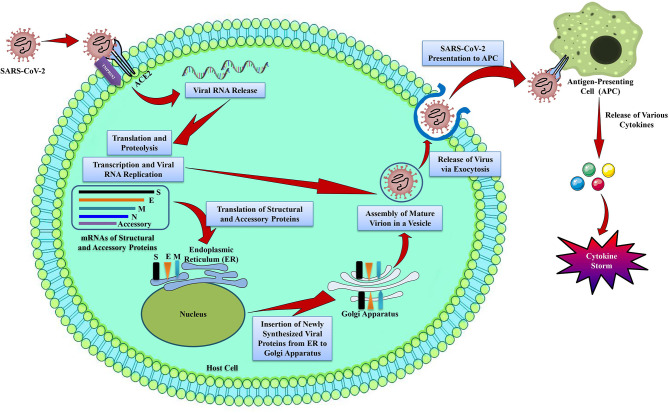
Figure 1.
The life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. SARS-CoV-2 contains 4 structural proteins including spike (S), envelope (E), matrix/membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N), in association with various accessory proteins. SARS-CoV-2 enters into the host cell by binding with the S protein of the virus to the ACE2 receptor on the host cell. It has been found that S protein is cleaved into S1 and S2 by a cell-derived protease, where S1 binds with ACE2 receptor, and S2 is activated by the host serine protease TMPRSS2 and results in a fusion with the cell membrane. Following the entry into the host cell, SARS-CoV-2 takeovers the host cell machinery to transcribe, replicate, and translate its RNA genome and structural proteins before being reassembled, encapsulated, and exocytosed from the host cell. Following exocytosis, SARS-CoV-2 is presented to host antigen presenting cells (APCs), which eventually leads to the generation of various cytokines including, TNF-α, CXCL-10, IL-1, and IL-6 (InvivoGen, 2020).