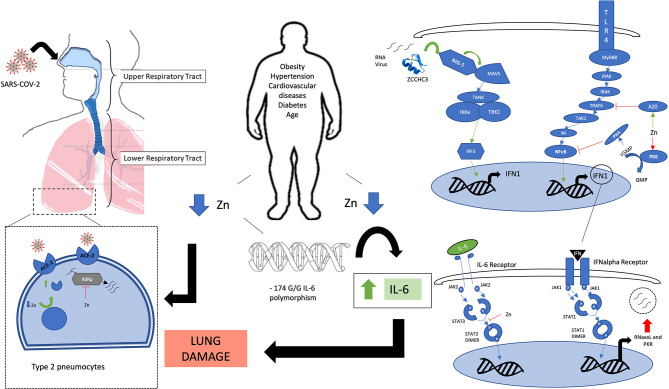
Figure 1.
Legend: A schematic view of the involvement of zinc in various signaling pathways. Green arrows: zinc-mediated activation. Red T bar arrows: zinc-mediated inhibition. Blue arrows: Flow of activation pathway. Obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and aging are associated with zinc deficiency. −174 GG polymorphism on the IL-6 promoter gene is associated with zinc homeostasis impairment and elevated IL-6 levels which contribute to lung damage. Zinc deficiency may increase ACE-2 receptor activity on type 2 pneumocytes and other cells that are infected by SARS-COV-2, mainly in the lower respiratory tract. Zinc inhibits RdRP, blocking viral RNA replication. Zinc-finger protein ZCCHC3 senses viral RNA and activates through RIG-1-like receptor a cascade that results in an increase in the interferon type 1 response. IFN type 1 stimulates synthesis of antiviral proteins such as RNaseL and PKR. Zinc helps to regulate the same kind of responses by activating the A20 protein that inhibits TRAF6 downstream activation, and by inhibiting PDE, which results in increased levels of cGMP that will activate PKA that will inhibit NF-κB. Zinc also inhibits STAT-3 dimerization, blocking active STAT3 signaling from the IL-6 receptor. Acronyms: ZCCHC3: Zinc finger CCHC domain-containing protein 3. RIG-1, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; MAVS, Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; TANK, TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator; Iκkε, I kappa B kinase epsilon; TBK1, TANK binding kinase 1; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; TLR, Toll-like receptor; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary-response protein 88; IRAK, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; TRAF-6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; TAK1: IKK, I kappa B kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; A20, zinc protein; PDE, phosphodiesterase; cGMP, cyclic guanosine-monophosphate; GMP, guanosine-monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; INF-1, interferon type 1; JAK, janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; RNase L, Ribonuclease L; PKR, RNA-activated protein kinase; ACE-2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.