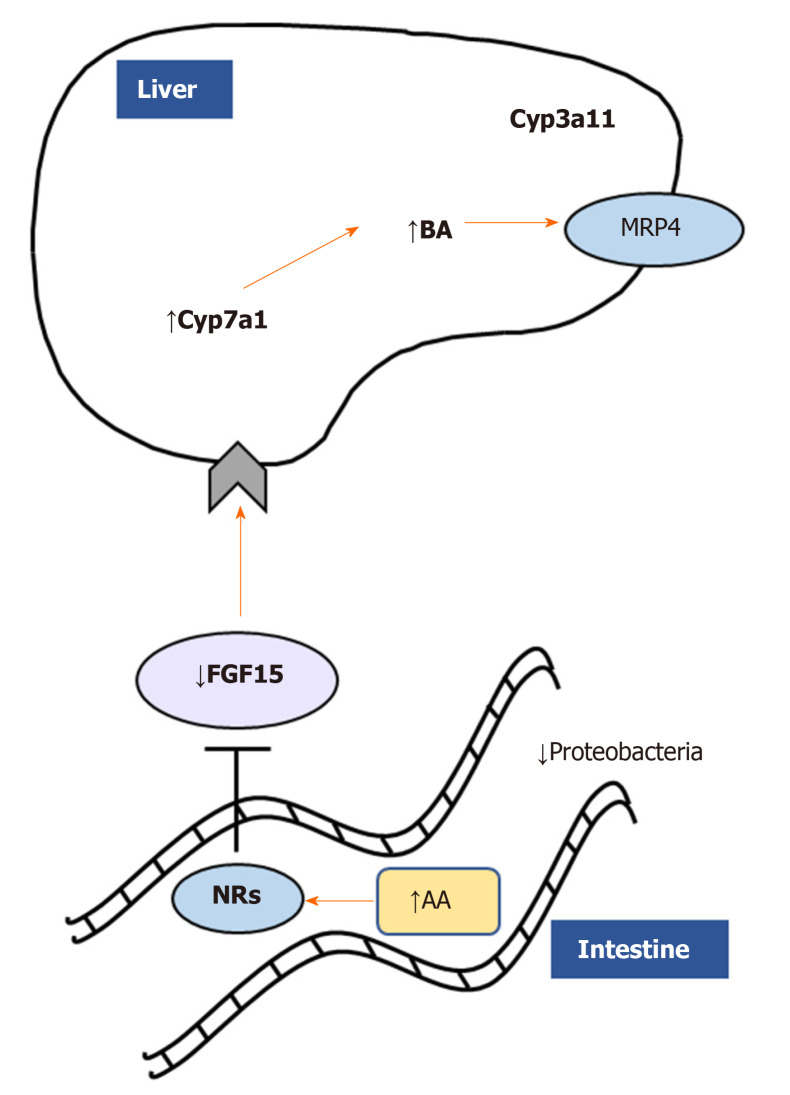
Figure 3.
Monoacylglycerol lipase deletion impacts gut-liver axis via nuclear receptor and microbiome modulation. Monoacylglycerol lipase ablation ameliorates cholestatic liver disease induced by 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine challenge diminishing fibrosis, inflammation, and fatty acid metabolism/oxidation in the liver. Accumulation of arachidonic acid binds nuclear receptors such as farnesoid X receptor, downregulating in turn fibroblast growth factor 15 and inducing bile acids synthesis and detoxification as shown by Cyp7a1/Cyp3a11. In addition, proinflammatory Proteobacteria were diminished in feces from Mgl-/- mice. AA: Arachidonic acid; NRs: Nuclear receptors; FGF15: Fibroblast growth factor 15; BA: Bile acids.