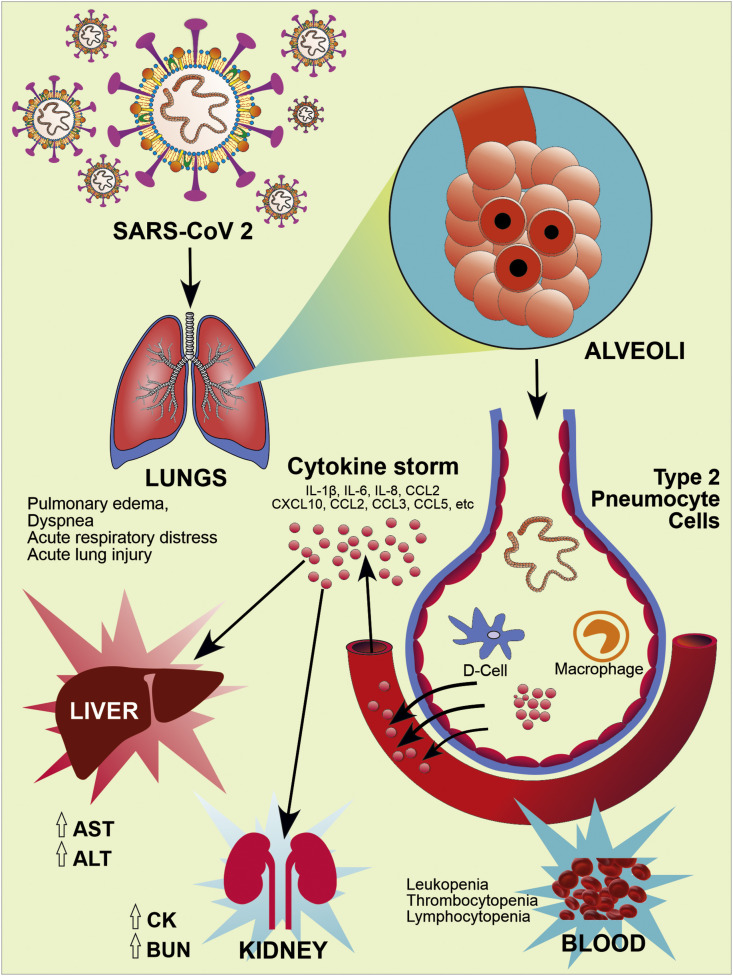
Fig. 4.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestation of COVID-19. RBD of S1 subunit of spike glycoproteins on the envelope of SARS-CoV-2 binds to the human hACE2 receptor, particularly in type-2 pneumocytes of lung tissue, and causes lung injury. ACE2 receptors expressed on other tissues like oral mucosa, vascular endothelial cells, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, heart, blood vessels also prone to infection. Further, SARS-CoV-2 infection activates host innate and adaptive immune response. Uncontrolled dysregulation of the host immune response against infection may cause the releases of excessive pro-inflammatory mediators and lead to the cytokine storm. It causes harmful tissue damage at the systemic level.