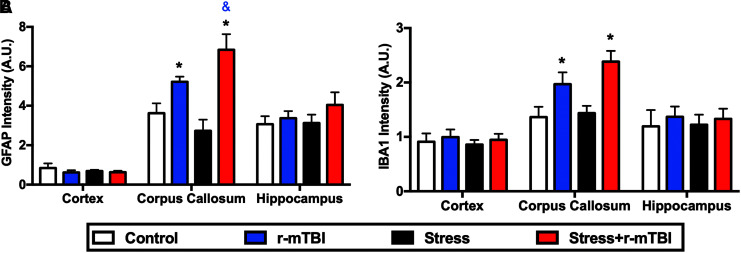
FIG. 6.
Effect of stress on brain injury markers at 3 months after the second repeated unpredictable stress. Quantitative assessments of ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunostaining in different brain regions are depicted in (A) and (B), respectively. Levels of Iba1 (A) and GFAP (B) were upregulated at 3 months after the last injury in the corpus callosum of repeated mild traumatic brain injury (r-mTBI) and stress+r-mTBI animals. Stress increases astrogliosis in injured animals as demonstrated by increased levels of GFAP immunostaining in the stress+r-mTBI group relative to the r-mTBI-only group (B). No changes in GFAP or Iba1 were observed in the cortex or the hippocampus (A, B). Data in each region in (A) and (B) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by two-stage linear step-up procedure of Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli to correct for multiple comparisons (n = 5–6). Statistically significant discoveries versus the control group are denoted by “*”, while statistically significant discoveries versus the r-mTBI group are denoted by “&”. Color image is available online.