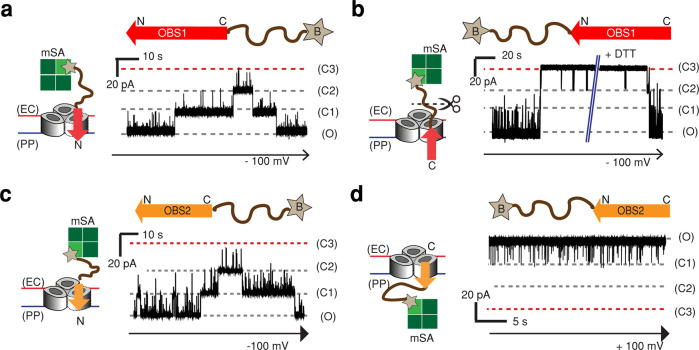
Figure 2.
Directional binding of OBS peptides to OmpF. Representative current traces of a single OmpF porin in the presence of OBS peptides capped either at (a, c) the C-terminus or (b, d) the N-terminus. The C-terminus-capped OBS1 and OBS2 constructs contain a 12-amino-acid SG linker (SSGGSSGGSSGG, brown curved line) and a single Cys residue with a cleavable linker (HPDP) downstream of the respective OBS sequence. (See the Methods section.) The N-terminus-capped OBS constructs have the same structures upstream of the OBS sequences. The Cys residue was biotinylated (star) and bound to monovalent streptavidin (mSA, green squares) in a 1:1 ratio to form OBS–mSA (C-terminus-capped) or mSA–OBS (N-terminus-capped). (a) Current trace of OmpF in the presence of OBS1–mSA (2.8 μM) at the extracellular surface at −100 mV. (b) Current trace of OmpF in the presence of mSA–OBS1 (2 μM) at the extracellular surface at −100 mV. Upon the addition of 10 mM DTT, the linker between the biotin and SG linker was cleaved, and OmpF returned to the fully open level. (c) Current trace of OmpF in the presence of OBS2–mSA (5 μM) at the extracellular surface at −100 mV. (d) Current trace of OmpF in the presence of mSA–OBS2 (1 μM) at the periplasmic surface at +100 mV.