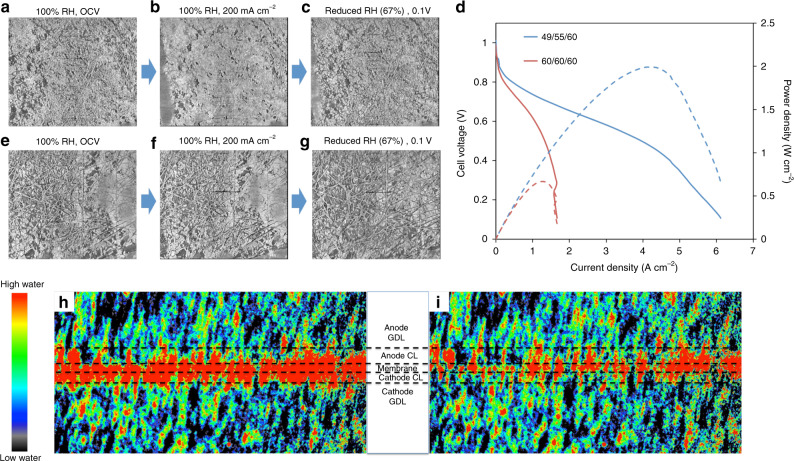
Fig. 2. Dew point effects on electrode water and cell behavior.
Operando micro X-ray computed tomography (CT) scans of the interface between the GDL and CL of (a–c) PtRu/C anodes and (e–f) Pt/C cathodes at conditions of: 100% RH at open circuit voltage (OCV), 100% RH at 200 mA cm−2, and reduced RH (67%) at 0.1 V, respectively. The H2/O2 flow rates were both kept at 0.2 L min−1. The cell temperature was kept at 28 °C (Polarization data for the operando cell is provided in Supplementary Fig. 5. d i-V (solid line) and i-power density curves (dashed line) at two different dew point configurations in 5 cm2 AMFCs. The membranes used in all tests were HDPE5. The 5 cm2 cells were tested at 60 °C with H2/O2 flows of 1 L/min. Operando neutron imaging of AMFCs at two different dew point situations: (h) The “full humidity” situation, which shows flooding inside the cell; (i) The “reduced dew points” situation, which shows drying out inside the cell. Anodes and cathodes used in the above three experiments had catalys loadings of 0.70 mgPtRu cm−2 and 0.60 mgPt cm−2, respectively.