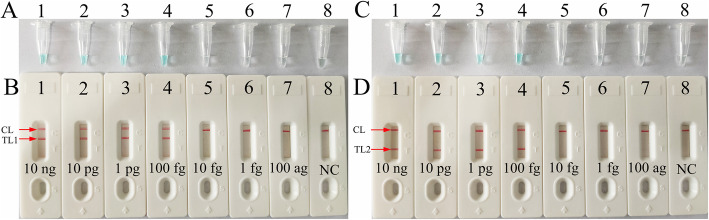
Fig. 4.
Sensitivity analysis of femA-LAMP (a, b) and mecA-LAMP (c, d) detection with serial dilutions of genomic DNA extracted from MSSA and MRSA strains, respectively
Two detection methods involving a colorimetric indictor (MG; a, c) or lateral flow biosensor (b, d) were used to analyze the amplification products. The genomic DNA was serially diluted (10 ng, 10 pg, 1 pg, 100 fg, 10 fg, 1 fg and 100 ag per microliter) and subjected to standard LAMP. Tubes A1-A7 (Biosensors B1-B7), S. aureus (ATCC25923) genomic templates (10 ng-100 ag); Tube A8 (Biosensor B8), negative control (DW). The LoD of femA-LAMP detection was 100 fg of genomic template per reaction. Tubes C1-C7 (Biosensors D1-D7), methicillin-resistant S. aureus (ATCC43300) genomic templates (10 ng-100 ag); Tube C8 (Biosensor D8), blank control (DW). The LoD of mecA-LAMP detection was 100 fg of genomic template per reaction.