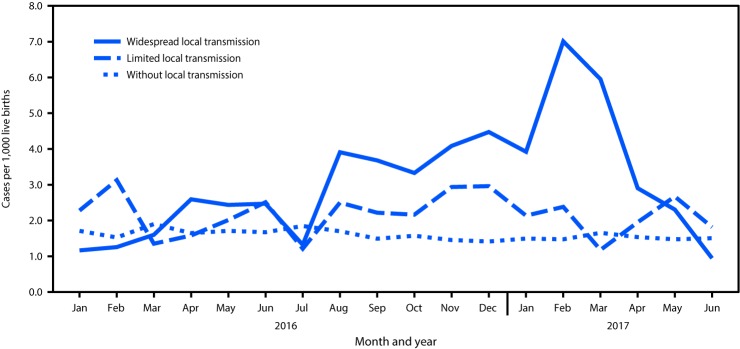
FIGURE.
Prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection during pregnancy,* by level of local Zika virus transmission and month — 22 U.S. jurisdictions, January 2016–June 2017†,§,¶
* Fetuses and infants included those with 1) brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or 2) eye abnormalities without mention of a brain abnormality included in brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly category.
† Jurisdictions with widespread local transmission of Zika virus during 2016–2017 included Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
§ Jurisdictions with limited local transmission of Zika virus during 2016–2017 included southern Florida counties and Texas Public Health Region 11.
¶ Jurisdictions without local transmission of Zika virus during 2016–2017 included California (selected counties), Georgia (selected metropolitan Atlanta counties), Hawaii, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York (excluding New York City residents), North Carolina (selected regions), Oklahoma, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Texas Public Health Region 10, Utah, Vermont, and Virginia.