Figure 1.
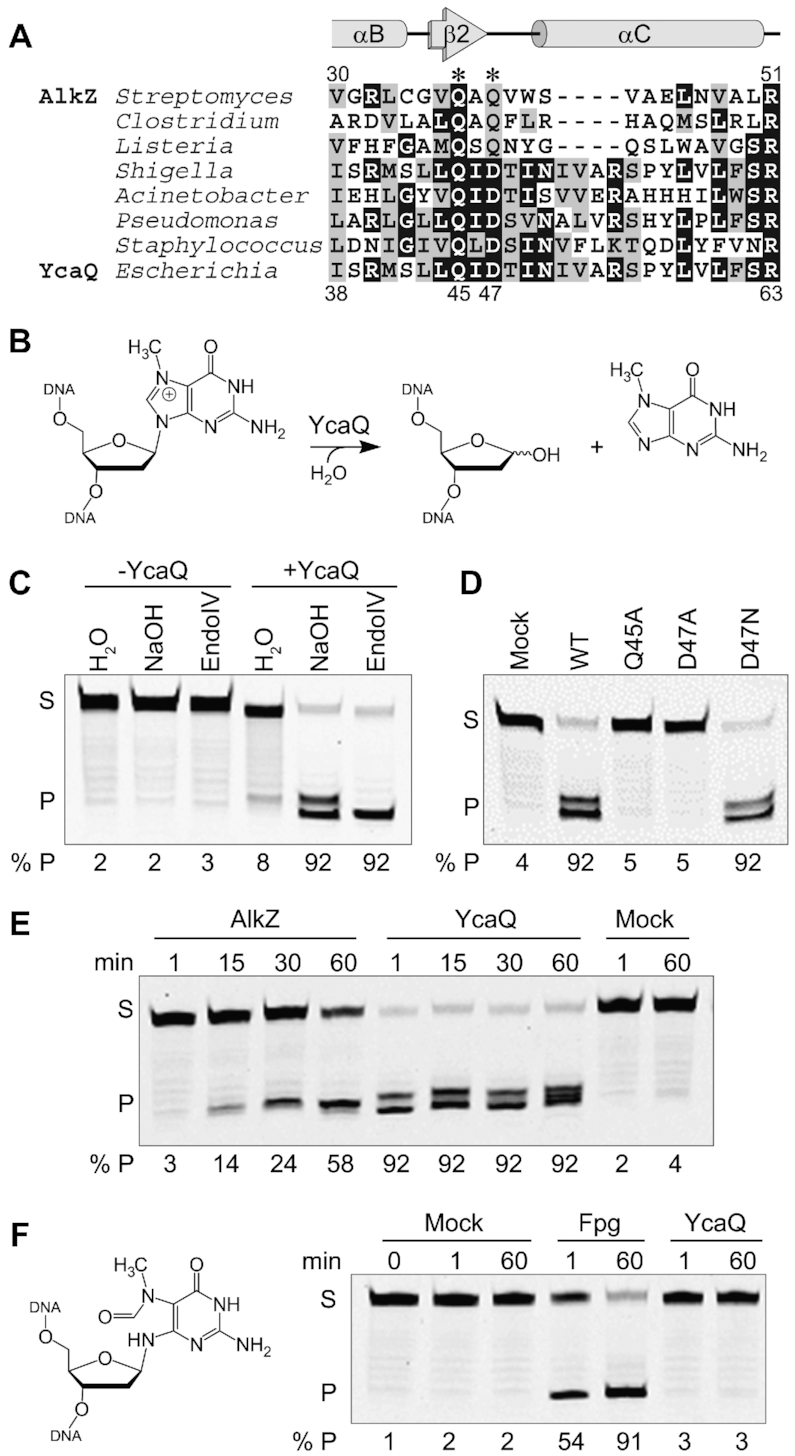
YcaQ is a Monofunctional DNA Glycosylase Specific for Cationic N-Alkylpurines. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of AlkZ/YcaQ homologs from Streptomyces sahachiroi and representative pathogens. Catalytic residues in AlkZ are labeled with asterisks. Secondary structures derived from the AlkZ crystal structure are shown above the alignment. (B) Schematic of d7mG base excision reaction. (C–F) Denaturing PAGE of 5′-FAM labeled d7mG-DNA substrate (S) and nicked AP-DNA product (P) after treatment with enzyme or buffer (mock). AP-DNA resulting from glycosylase activity was nicked by treatment with either 0.1 M NaOH (C–F) or EndoIV (C) to produce β- and β,δ-elimination products, which are quantified below each gel. (C) d7mG-DNA was incubated with (+) or without (-) YcaQ for 1 hr followed by treatment with either water, NaOH, or EndoIV. (D) Comparison of WT and mutant YcaQ activity after 1 hr. (E) Time-dependence of d7mG excision by AlkZ and YcaQ. The presence of a single product band in the AlkZ reaction is likely a result of EndoIV contamination in the work-up buffer, consistent with our previous analysis (20). (F) Structure and excision of mFaPy-dG DNA, treated with E. coli Fpg, YcaQ, or buffer for the specified time, followed by alkaline hydrolysis.
