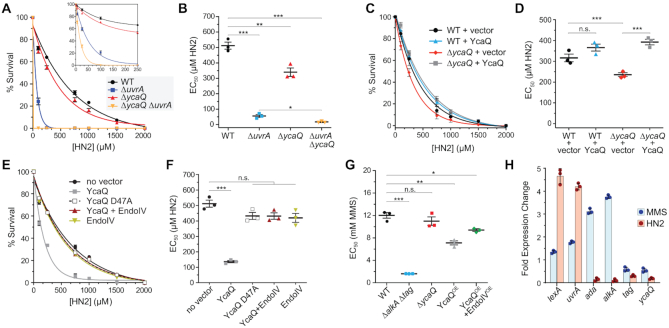
Figure 6.
Deletion and overexpression of YcaQ sensitizes E. coli to mechlorethamine. (A) Colony dilution assay for E. coli deletion strains exposed to increasing concentrations of mechlorethamine (HN2). Values are mean ± SEM (n = 3). Percent (%) survival is relative to untreated cells. (B) EC50 values derived from data in panel A. Significance values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA (*P = 0.0140; **P = 0.0085; ***P < 0.0001; n.s, not significant). (C) Colony dilution assay for E. coli strains complimented with YcaQ or empty vector. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 3). (D) Quantification of the data shown in panel D. One-way ANOVA values: ***P = 0.0004, n.s., not significant. (E) Colony dilution assay showing the effect of mechlorethamine (HN2) on wild-type E. coli overexpressing YcaQ variants and/or EndoIV. (F) Quantification of the data shown in panel E. One-way ANOVA significance values: *P = 0.0088; **P = 0.0013; ***P < 0.0001; n.s, not significant. (G) MMS EC50 values (mM) for various E. coli deletion (Δ) or over-expression (OE) strains. (H) qRT-PCR results of DNA repair genes after treatment of E. coli with 5 mM MMS or 200 μM mechlorethamine (HN2) for 2 hr. Average ± SEM for three biological replicates.