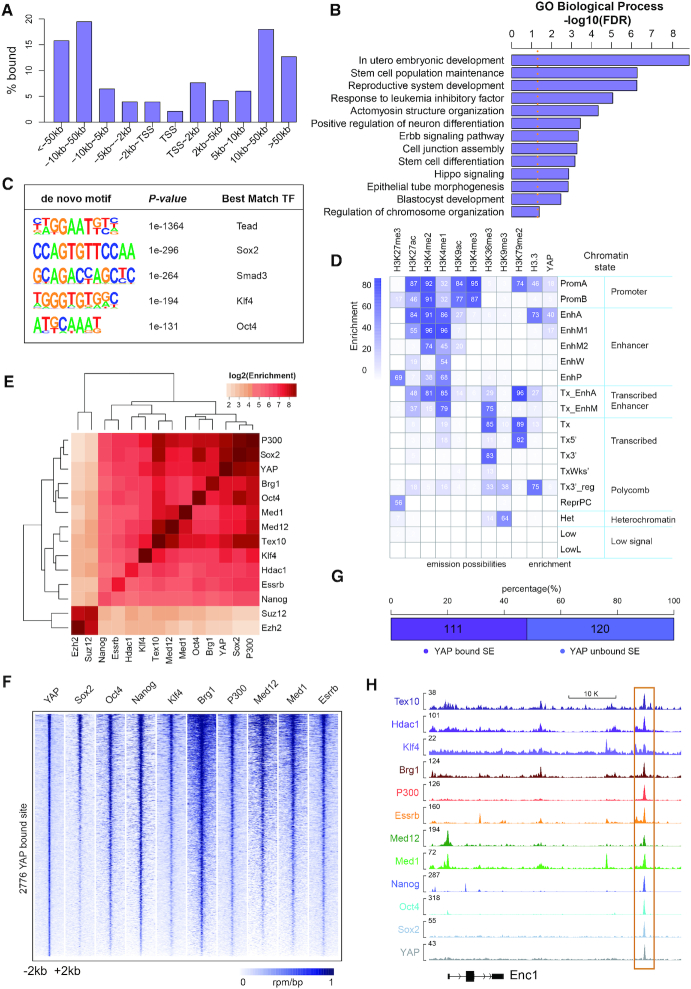
Figure 2.
YAP predominantly binds to distal regions from transcription start site (TSS) and shows high correlation with super-enhancer associated factors. (A) Distribution of YAP ChIP-seq peaks with respect to the TSSs in WT ESCs. (B) GO analysis of genes with YAP enrichment within 50kb of their TSSs in WT ESCs. (C) De novo motif analysis of YAP peaks. (D) YAP enrichment at chromatin sites defined by ChromHMM. Chromatin states and their mnemonics are represented in row. The frequency of indicated histone epigenetic marks and variant at each chromatin state represented as ChromHMM emission probabilities is showed in column. Enrichment is marked from blue (highest) to white (lowest). (E) Heatmap demonstrating the enrichment of co-localization between the peaks of YAP and core pluripotency factors, epigenetic modifiers and SE related factors in WT ESCs. Hierarchical clustering dendrograms are shown at the top and left of the heatmap. (F) Heatmaps of normalized ChIP-seq signal for Sox2, Oct4, Nanog, Klf4, Brg1, P300, Med12, Med1 and Esrrb at all YAP bound loci in WT ESCs. (G) Stacked bar plot showing the proportion of YAP bound and unbound SEs among 231 high-confidence SEs reported in mouse ESCs. (H) ChIP-seq signal tracks of YAP and SE related factors at Enc1 distal enhancer in WT ESCs.