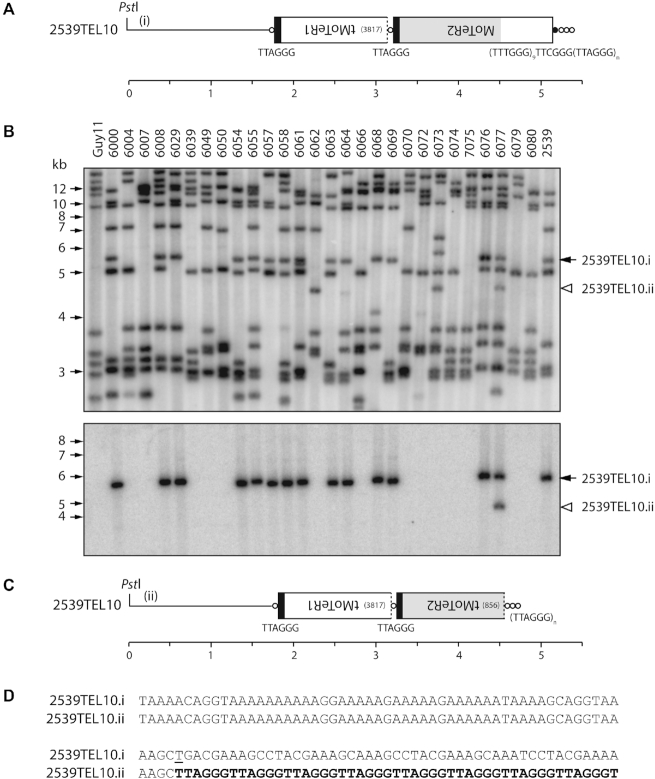
Figure 7.
Simple terminal truncations. (A) Telomeric PstI fragment containing 2539TEL10 showing MoTeR sequences embedded in the telomere. (B) TRF segregation among progeny of a cross between 2539 (MoTeR+) and Guy11 (MoTeR−). The top panel shows the phosphorimage of a Southern hybridization analysis of PstI-digested DNAs probed with telomere repeats. Parental strain DNAs are loaded in the outermost lanes, with progeny DNAs in between. 2539TEL10.i is marked with a black arrowhead. A white arrowhead marks a novel TRF that corresponds to a TEL10 variant (ii). Bottom panel: the membrane used in A was stripped and re-hybridized with a MoTeR2 probe. (C) Organization of 2539TEL10.ii showing 5′-truncation of the terminal MoTeR2. (D) 106 bp of sequence surrounding the site of de novo telomere addition at the MoTeR2 truncation boundary. Telomere repeats are highlighted with bold text. A ‘T’ nucleotide that seeded the de novo telomere addition is underlined. Inferred rearrangement mechanism: i → ii) MoTeR truncation, de novo telomere formation.