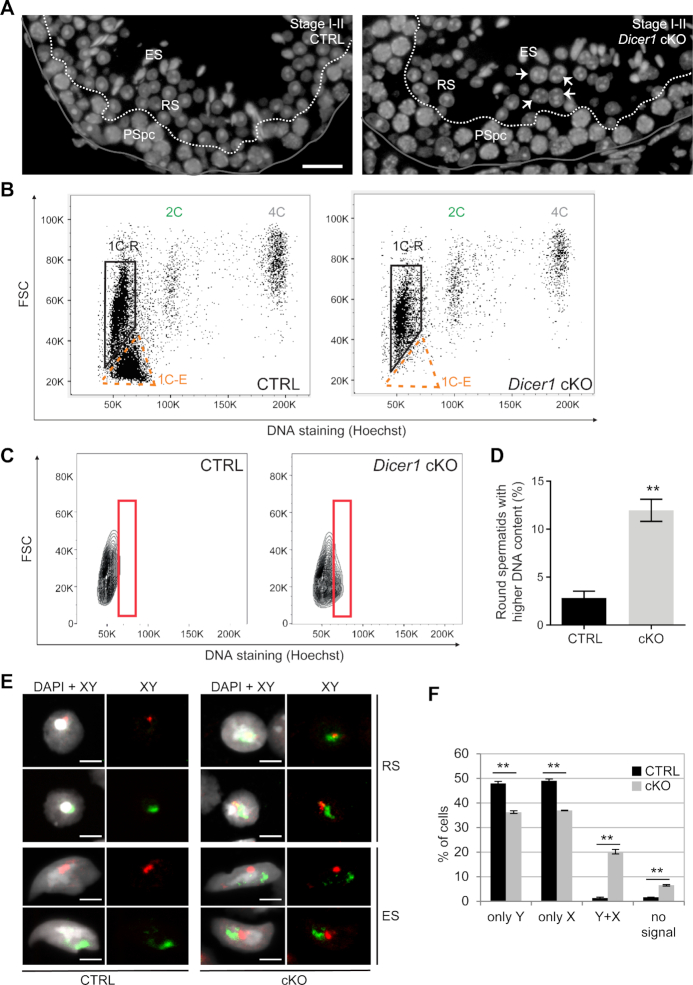
Figure 7.
Meiotic chromosome segregation is defective in Dicer1 knockout germ cells. (A) Nuclei of early round spermatids at stage I-II appear unevenly sized in Dicer1 cKO testes compared to control (CTRL). Nuclei were stained by DAPI (grey). Basal lamina is indicated with a grey line. The border between pachytene spermatocyte (PSpc) and round spermatid (RS) layers is indicated with a dashed white line. ES, elongating spermatids. Some examples of abnormally large spermatid nuclei are indicated with white arrows. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) A representative Hoechst 33342 live-cell fluorescent DNA staining and flow cytometric analysis of DNA ploidy for testicular cells isolated from CTRL and Dicer1 cKO mice. Dicer1 cKO testes display the expected 1C, 2C and 4C populations but specifically lack the elongating spermatid population. 1C-R, round spermatids; 1C–E, elongating spermatids; 2C, diploid cells; 4C, tetraploid cells; FSC, forward scatter light. See also Supplementary Figure S6. (C, D) An in-depth analysis of the 1C-R population reveals that the number of round spermatids having a higher DNA content is significantly higher in Dicer1 cKO than in CTRL, n = 3, SEM, ** P< 0.01. (E) DNA in situ hybridization revealed abnormal number of sex chromosomes in Dicer1 cKO haploid spermatids. Round spermatid (RS) and elongating spermatid (ES) nuclei containing both X (red) and Y (green) chromosome signals were frequently detected in cKO. Nuclei were stained by DAPI. Scale bar: 5 μm. (F) Quantification of the X and Y chromosome signals in Dicer1 cKO vs. CTRL round spermatids (more than 500 cells per mouse were counted); n = 2, SEM, **P< 0.01.