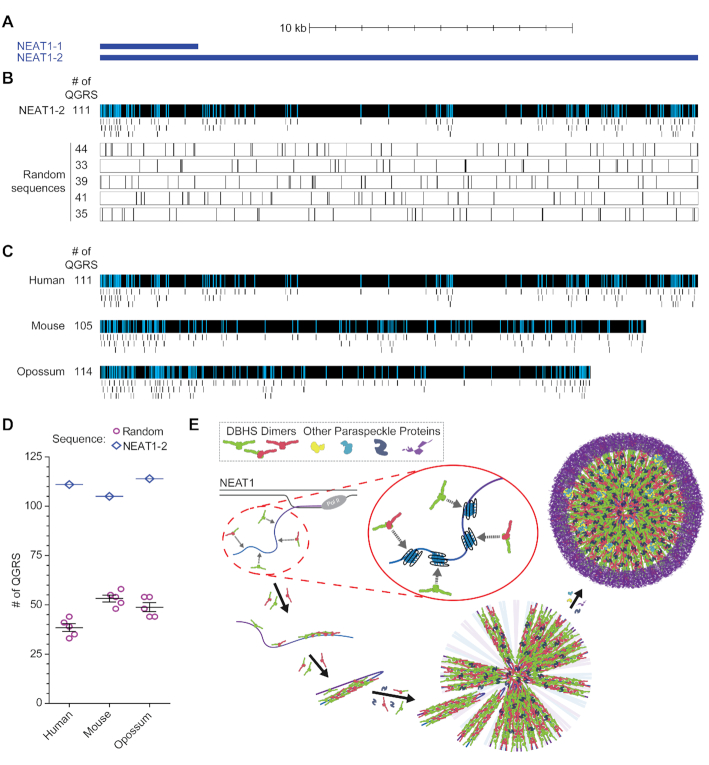
Figure 7.
Enrichment in G-quadruplex motifs is a conserved feature of NEAT1 homologues. (A) Human NEAT1 isoforms and scale bar. (B) Quadruplex-forming G-rich sequences (QGRS) on human NEAT1 (upper track) and on randomly generated sequences (lower tracks). QGRS are shown mapped to NEAT1 (upper track, light blue bars) and expanded below (upper track, short black bars). QGRS (tall black bars) were identified for five randomly generated sequences with length and GC content equal to NEAT1 (lower tracks). The number of QGRS identified on each sequence is shown to the left of the corresponding track. (C) Quadruplex-forming G-rich sequences predicted along the length of NEAT1 homologues. Identified QGRS are shown mapped to each NEAT1 homologue (light blue bars) and expanded below (short black bars). (D) QGRS enrichment among NEAT1 homologues. Sequences were randomly generated with the length and GC content of NEAT1 homologues and QGRS were identified. For each homologue, numbers of QGRS on five generated sequences are plotted with mean and SEM, with the number of QGRS on the corresponding homologue plotted for comparison. (E) Paraspeckle assembly begins with co-transcriptional recruitment of DBHS dimers (NONO and SFPQ homo- and heterodimers) to NEAT1, seeding formation of NEAT1 RNPs, the primary subunit of paraspeckles, and initiating paraspeckle formation. The elements of NEAT1 responsible for this recruitment have yet to be identified. G-quadruplex structures along the length of NEAT1 are recognized by NONO with structural specificity, play a critical role in NONO-NEAT1 association, and are a conserved feature among NEAT1 homologues. These findings position NEAT1 G-quadruplexes as a primary candidate for the NONO-recruiting elements of NEAT1.